| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
柚皮苷
CAS:10236-47-2 |
|
 |
甲酸
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
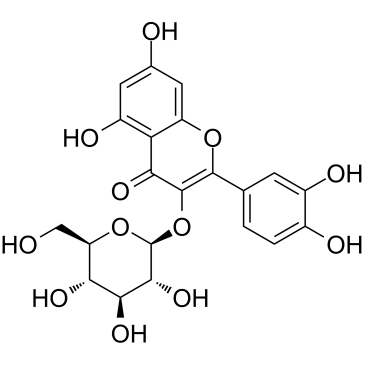 |
异槲皮苷
CAS:482-35-9 |
|
 |
柚皮素
CAS:67604-48-2 |
|
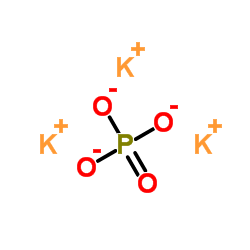 |
磷酸钾
CAS:7778-53-2 |