| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
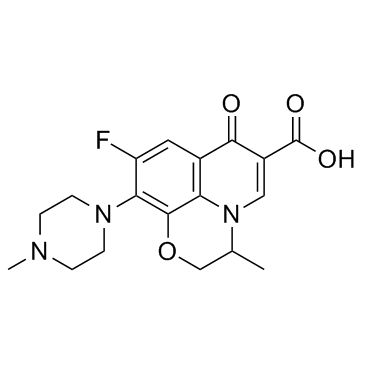 |
氧氟沙星
CAS:82419-36-1 |
|
 |
L-尼古丁
CAS:54-11-5 |
|
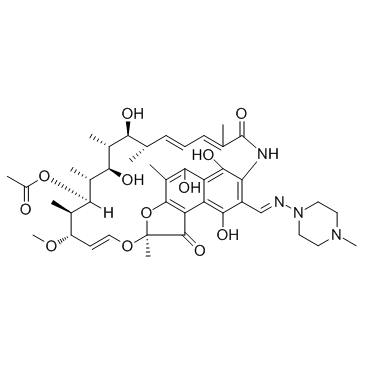 |
利福平
CAS:13292-46-1 |
|
 |
沙丁胺醇
CAS:18559-94-9 |
|
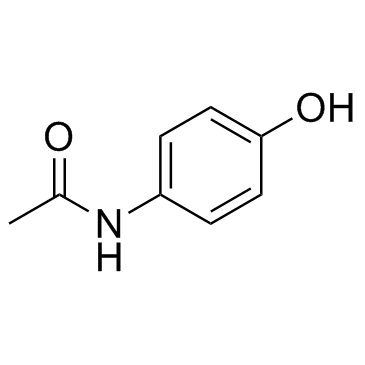 |
对乙酰氨基苯酚
CAS:103-90-2 |
|
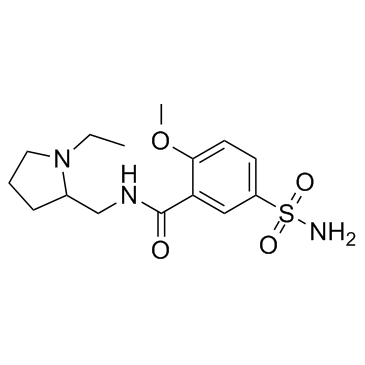 |
舒必利
CAS:15676-16-1 |
|
 |
红霉素
CAS:114-07-8 |
|
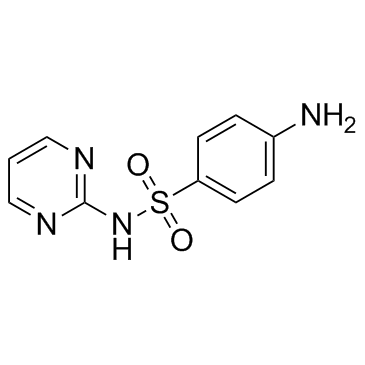 |
磺胺嘧啶
CAS:68-35-9 |
|
 |
环孢霉素A
CAS:59865-13-3 |
|
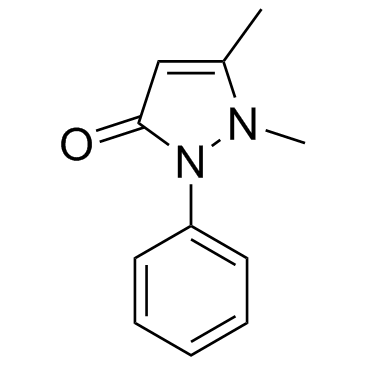 |
安替比林
CAS:60-80-0 |