| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
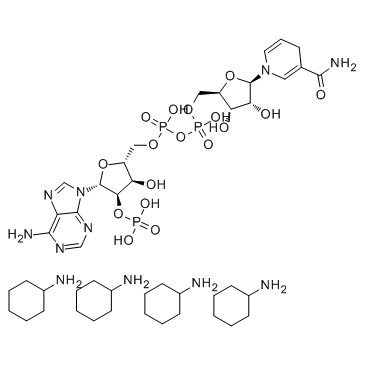
三磷酸吡啶核苷酸 钠盐 水合物
CAS:698999-85-8 |
|
 |
还原型辅酶II四钠
CAS:100929-71-3 |
|
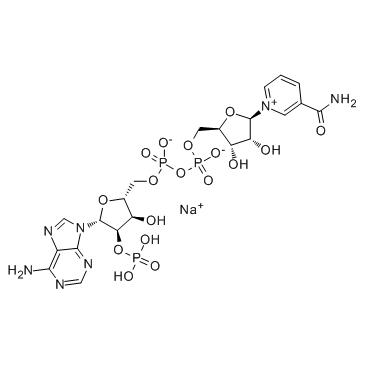 |
β-烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸钠盐
CAS:1184-16-3 |