| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
十二烷基硫酸钠
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
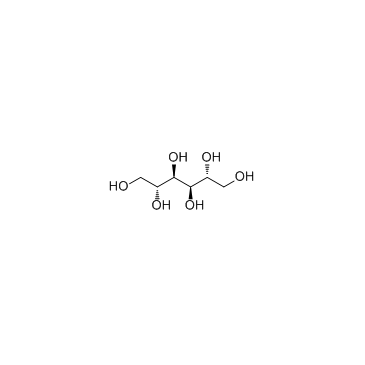 |
甘露醇
CAS:69-65-8 |
|
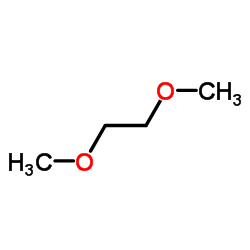 |
乙二醇二甲醚
CAS:110-71-4 |
|
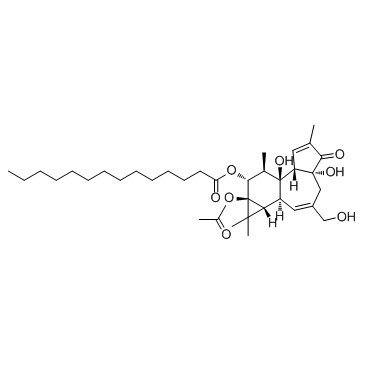 |
12-O-十四烷酰佛波醋酸酯-13
CAS:16561-29-8 |
|
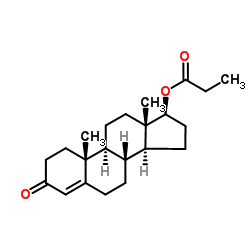 |
丙酸睾丸酮
CAS:57-85-2 |