| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
酪胺盐酸盐
CAS:59880-97-6 |
|
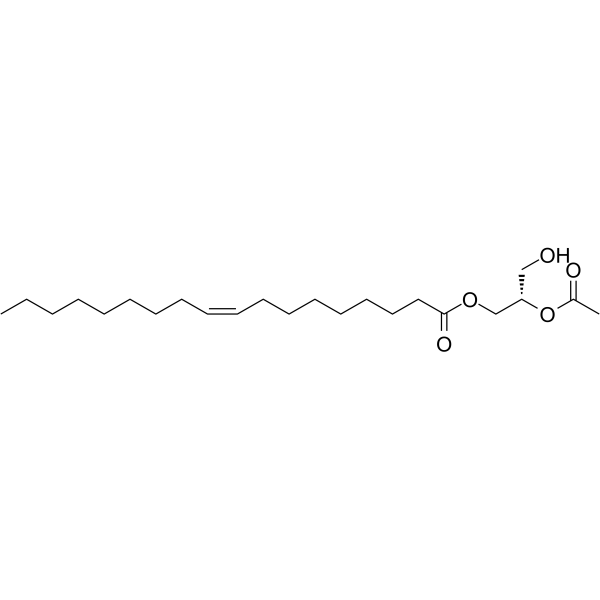 |
1-油酰基-2-乙酰基-sn-丙三醇
CAS:86390-77-4 |
|
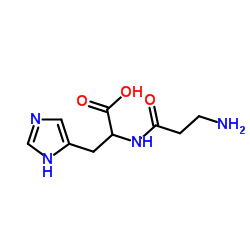 |
磷脂酶D 来源于色褐链霉菌
CAS:9001-87-0 |
|
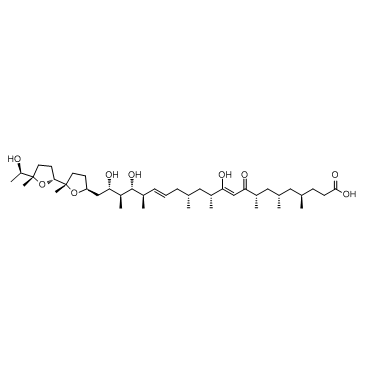 |
离子霉素
CAS:56092-81-0 |