| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
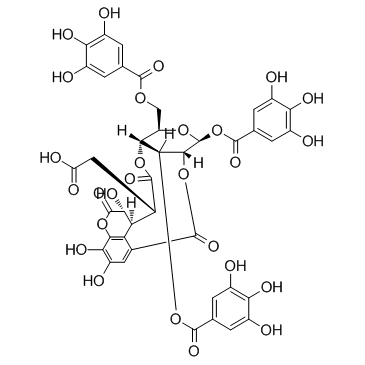 |
诃子林鞣酸
CAS:18942-26-2 |
|
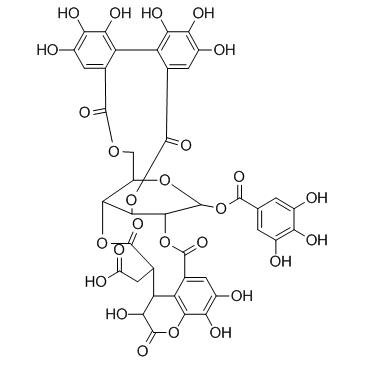 |
诃子鞣酸
CAS:23094-71-5 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
诃子林鞣酸
CAS:18942-26-2 |
|
 |
诃子鞣酸
CAS:23094-71-5 |