| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
布洛芬
CAS:15687-27-1 |
|
 |
酮洛芬
CAS:22071-15-4 |
|
 |
地塞米松
CAS:50-02-2 |
|
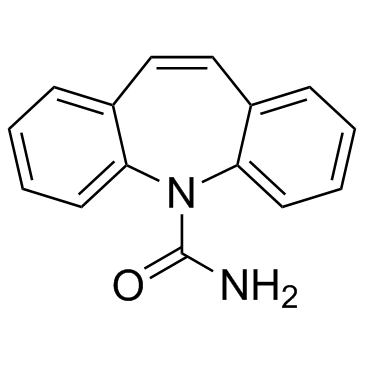 |
卡马西平
CAS:298-46-4 |
|
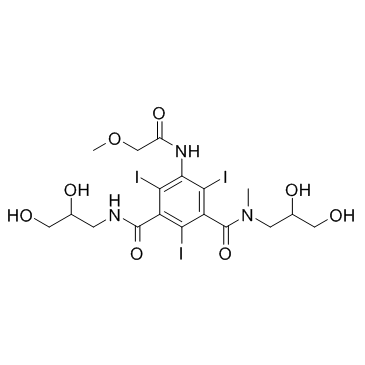 |
碘普罗胺
CAS:73334-07-3 |