| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
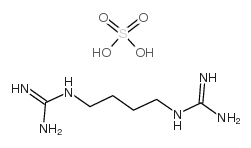 |
硫酸魁蛤素
CAS:14923-17-2 |
|
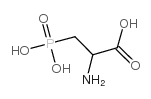 |
DL-2-氨基-3-膦酸丙酸(AP3)
CAS:20263-06-3 |