| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
(S)-α-氨基-3-羟基-5-甲基异恶唑-4-丙酸
CAS:83643-88-3 |
|
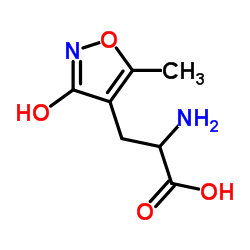 |
(±)-Α-氨基-3-羟基-5-甲基异恶唑-4-丙酸
CAS:74341-63-2 |