| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
核苷5′-二磷酸激酶
CAS:9026-51-1 |
|
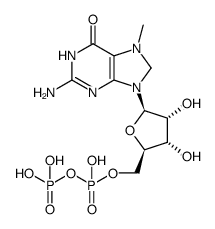 |
7-Methylguanosine 5'-diphosphate sodium
CAS:104809-16-7 |