| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
焦磷酸四乙酯
CAS:107-49-3 |
|
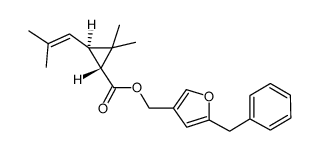 |
生物苄呋菊酯
CAS:28434-01-7 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
焦磷酸四乙酯
CAS:107-49-3 |
|
 |
生物苄呋菊酯
CAS:28434-01-7 |