| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Tetraethyl pyrophosphate
CAS:107-49-3 |
|
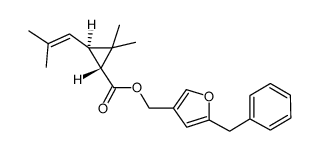 |
BIORESMETHRIN
CAS:28434-01-7 |