A fast and reliable spectroscopic method for the determination of membrane--water partition coefficients of organic compounds.
B de Castro, P Gameiro, J L Lima, C Matos, S Reis
文献索引:Lipids 36(1) , 89-96, (2001)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Partition coefficients (Kp) between egg yolk phosphatidylcholine multilamellar vesicles and water were determined for two nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin and acemetacin) using two independent methodologies: derivative spectrophotometry and variation of the experimental acidity constant in the presence of increasing vesicle concentration. Second-derivative spectrophotometry allowed for total elimination of background signal effects arising from lipid vesicles, without the need for separation techniques that may disturb equilibrium states. By using a model based on a simple partition, the values of K(T)p can be obtained directly; furthermore, by performing determinations at two different pH values it is possible to calculate partition coefficients for the neutral and negatively charged forms of the drugs (K(AH)p and K(A)p). In the other methodology, values of apparent acidity constants (K(app)) were determined by spectrophotometry at different pH values and different lipid concentrations, and an increase in K(app) with decreasing lipid concentration was observed for both drugs, and from this dependence it was possible to calculate K(AH)p and K(A-)p for each drug. These values were used as a check for those obtained by derivative spectroscopy, which has proven to be a reliable and more expeditious method to obtain K(AH)p and K(A-)p .
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
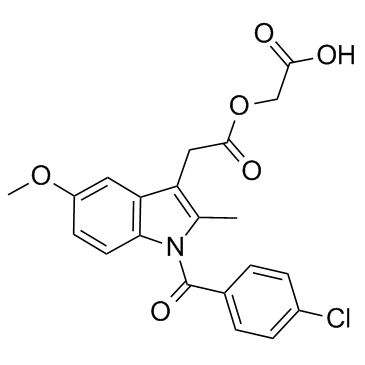 |
阿西美辛
CAS:53164-05-9 |
C21H18ClNO6 |
|
A comparison of low-molecular-weight heparin and combined th...
2009-04-01 [Phlebology 24(2) , 56-60, (2009)] |
|
Multivariate optimization of separation conditions for simul...
2013-01-01 [J. AOAC Int. 96(4) , 723-9, (2013)] |
|
Pharmacokinetics of acemetacin and its active metabolite ind...
2009-01-01 [Ann. Hepatol. 8(2) , 141-7, (2009)] |
|
[Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint. Efficacy and...
2004-09-01 [Orthopade. 33(9) , 1032-41, (2004)] |
|
Bartter's Syndrome with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
2009-01-01 [J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 72(2) , 88-90, (2009)] |