[Consistence of the radial artery as a conduit used in aortocoronary bypass surgery, a possibility of preventing shunt spasm].
T M Ripp, D S Kondrat'eva, V F Mordovin, S A Afanas'ev, B N Kozlov, T E Suslova
文献索引:Ter. Arkh. 84(12) , 13-7, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
To develop a new procedure to evaluate the functional consistence of the radial artery (RA) as a conduit used in aortocoronary bypass surgery (ACBS), to verify the prognostic value of the changed diameter of RA, and to prevent its spasm.The study enrolled 34 patients aged 59.4 +/- 8.6 years with coronary artery stenoses, who underwent ACBS using a RA conduit. While preparing them for surgery, endothelium-dependent vasodilation (EDVD) of RA, i.e. the magnitude of a change in its diameter (deltaD) was assessed; RA tone and nitric oxide (NO) concentrations were estimated during surgery; RA EDVD was re-estimated in 12 lercanidipine-treated patients with deltaD < 8%.The patients were primarily divided into 2 groups: 1) deltaD > or = 8% (RA spasm intra- and postoperatively); 2) EDVD deltaD < 8% (RA spasm). Significant differences between Groups 1 and 2 were intraoperatively recorded in vascular wall tone (U = 1.0; Z = -2.3; p = 0.02) and NO concentrations (p = 0.0); a relationship was found between these parameters. After lercanidipine treatment, the degree of deltaD = 4.36 +/- 1.89% increased to 11.32 +/- 2.22% (p = 0.0) and RA tone dropped from -1.68 to -3.9 mm in Group 2a with the baseline decreased vasodilating activity of RA.Ultrasound assessment of the vasodilating activity of RA provides adequate evidence about its arterial wall tone during surgery. deltaD < 8% is prognostically unfavorable and serves as a contraindication to the use of RA as a conduit during ACBS. The administration of lercanidipine allows effective correction of the dilatory capacities of an arterial conduit.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
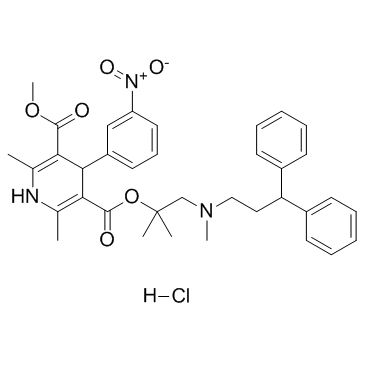 |
盐酸乐卡地平
CAS:132866-11-6 |
C36H42ClN3O6 |
|
Differences in lercanidipine systemic exposure when administ...
2012-07-01 [Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 68(7) , 1043-7, (2012)] |
|
Rationale for the use of a fixed-dose combination in the man...
2010-01-01 [Clin. Drug Investig. 30(12) , 843-54, (2010)] |
|
Lercanidipine rescues hippocampus pyramidal neurons from mil...
2011-05-01 [Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 31(4) , 561-7, (2011)] |
|
Incidence and clinical course of lercanidipine-associated cl...
2010-09-01 [Clin. Nephrol. 74(3) , 217-22, (2010)] |
|
Polymorphism of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene...
2012-06-01 [Gene 500(2) , 207-10, (2012)] |