A 1H NMR-based metabolomics approach for mechanistic insight into acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity.
Kiyoshi Fukuhara, Akiko Ohno, Yosuke Ando, Takashi Yamoto, Haruhiro Okuda
文献索引:Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 26(4) , 399-406, (2011)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The widely used analgesic-antipyretic drug acetaminophen (APAP) is known to cause serious liver necrosis at high doses in man and experimental animals. For studies of toxic processes, 1H NMR spectroscopy of biofluids allows monitoring of endogenous metabolite profiles that alter characteristically in response to changes in physiological status. Herein, a 1H NMR metabolomics approach was applied to the investigation of APAP toxicity in rats and the effect of phenobarbital (PB) on APAP-induced hepatotoxicity. Metabolite differences due to hepatotoxicity were observed in 1H NMR spectra of serum and urine, and enhanced APAP hepatotoxicity by pretreatment with PB was clearly shown by a principal components analysis of the spectral data. NMR spectra of APAP-dosed rat urine provided profiles of APAP-related compounds together with endogenous metabolites. By comparison of endogenous and APAP-related metabolite spectra with those from rats pretreated with PB, it was possible to show the importance of oxidative metabolism of APAP to N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone, an essential step in APAP hepatotoxicity.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
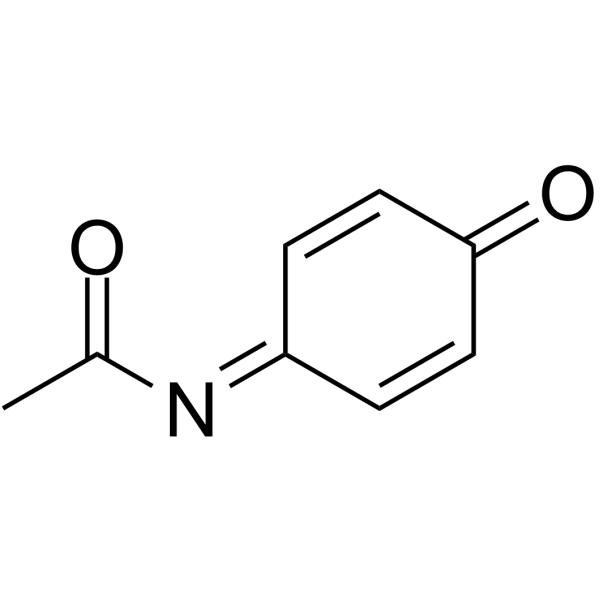 |
N-乙酰苯醌亚胺
CAS:50700-49-7 |
C8H7NO2 |
|
Targeting mitochondria with methylene blue protects mice aga...
2015-01-01 [Hepatology 61(1) , 326-36, (2015)] |
|
Monitoring paracetamol metabolism after single and repeated ...
2007-09-01 [Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 45(9) , 496-503, (2007)] |
|
Use of a systems model of drug-induced liver injury (DILIsym...
2014-04-21 [Toxicol. Lett. 226(2) , 163-72, (2014)] |
|
In-source formation ofN-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI),...
2011-01-01 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 879(17-18) , 1476-84, (2011)] |
|
Combination of electrochemistry and nuclear magnetic resonan...
2012-10-16 [Anal. Chem. 84(20) , 8777-82, (2012)] |