N-乙酰苯醌亚胺
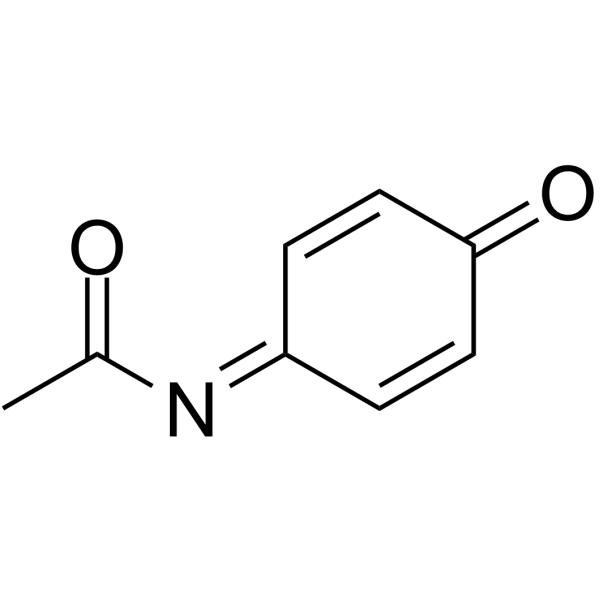
N-乙酰苯醌亚胺结构式

|
常用名 | N-乙酰苯醌亚胺 | 英文名 | N-Acetylimidoquinone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 50700-49-7 | 分子量 | 149.147 | |
| 密度 | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 255.6±43.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C8H7NO2 | 熔点 | 74-75ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 101.6±33.5 °C |
|
Targeting mitochondria with methylene blue protects mice against acetaminophen-induced liver injury.
Hepatology 61(1) , 326-36, (2015) Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose is a frequent cause of drug-induced liver injury and the most frequent cause of acute liver failure in the Western world. Previous studies with mouse models have revealed that impairment of mitochondrial respiration is an early e... |
|
|
Monitoring paracetamol metabolism after single and repeated administration in pediatric patients with neoplastic diseases.
Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 45(9) , 496-503, (2007) Paracetamol (PCM) is frequently used in pediatric patients with neoplastic disease. It is metabolized mainly by conjugation, but at therapeutic concentrations, a small fraction of the drug undergoes oxidative metabolism via cytochrome P450 forming the hepatot... |
|
|
Use of a systems model of drug-induced liver injury (DILIsym®) to elucidate the mechanistic differences between acetaminophen and its less-toxic isomer, AMAP, in mice
Toxicol. Lett. 226(2) , 163-72, (2014) Acetaminophen (APAP) has been used as a probe drug to investigate drug-induced liver injury (DILI). In mice, 3′-hydroxyacetanilide (AMAP), a less-toxic isomer of APAP, has also been studied as a negative control. Various mechanisms for the divergence in toxic... |
|
|
In-source formation ofN-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI), the putatively toxic acetaminophen (paracetamol) metabolite, after derivatization with pentafluorobenzyl bromide and GC–ECNICI-MS analysis
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 879(17-18) , 1476-84, (2011) Pentafluorobenzyl (PFB) bromide (PFB-Br) is a versatile derivatization reagent for numerous classes of compounds. Under electron-capture negative-ion chemical ionization (ECNICI) conditions PFB derivatives of acidic compounds readily and abundantly ionize to ... |
|
|
Combination of electrochemistry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for metabolism studies.
Anal. Chem. 84(20) , 8777-82, (2012) During the development of new materials demonstrating biological activity, prediction and identification of reactive intermediates generated in the course of drug metabolism in the human liver is of great importance. We present a rapid and purely instrumental... |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics of acetaminophen-protein adducts in adults with acetaminophen overdose and acute liver failure.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 37(8) , 1779-84, (2009) Acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver toxicity occurs with formation of APAP-protein adducts. These adducts are formed by hepatic metabolism of APAP to N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine, which covalently binds to hepatic proteins as 3-(cystein-S-yl)-APAP adducts. Ad... |
|
|
Acetaminophen bioactivation by human cytochrome P450 enzymes and animal microsomes.
Xenobiotica 39(1) , 11-21, (2009) Acetaminophen is a widely used analgesic antipyretic agent. When used at low doses, it is a safe drug, but at higher doses it can cause acute hepatic necrosis in humans and experimental animals. The key mechanism in the hepatotoxicity is cytochrome P450 (CYP)... |
|
|
Resistance to acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in glutathione S-transferase Mu 1-null mice.
J. Toxicol. Sci. 37(3) , 595-605, (2012) We investigated the role of glutathione S-transferases Mu 1 (GSTM1) in acetaminophen (APAP)-induced hepatotoxicity using Gstm1-null mice. A single oral administration of APAP resulted in a marked increase in plasma alanine aminotransferase accompanied by hepa... |
|
|
A 1H NMR-based metabolomics approach for mechanistic insight into acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity.
Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 26(4) , 399-406, (2011) The widely used analgesic-antipyretic drug acetaminophen (APAP) is known to cause serious liver necrosis at high doses in man and experimental animals. For studies of toxic processes, 1H NMR spectroscopy of biofluids allows monitoring of endogenous metabolite... |
|
|
Structural and kinetic analyses of macrophage migration inhibitory factor active site interactions.
Biochemistry 48(1) , 132-9, (2009) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is a secreted protein expressed in numerous cell types that counters the antiinflammatory effects of glucocorticoids and has been implicated in sepsis, cancer, and certain autoimmune diseases. Interestingly, the st... |