Identification of the Raf-1 signaling pathway used by cAMP to inhibit p42/p44 MAPK in rat lacrimal gland acini: role in potentiation of protein secretion.
Chika Funaki, Robin R Hodges, Darlene A Dartt
文献索引:Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 51(12) , 6321-8, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The lacrimal gland is primarily responsible for the aqueous portion of the tear film. Simultaneous addition of cholinergic agonists or growth factors with cAMP-dependent agonists potentiates secretion. Recent investigations revealed that cAMP decreases p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activity stimulated by cholinergic agonists and growth factors that could account for this potentiation. In this study the authors identify the signal transduction pathway used by cAMP to inhibit MAPK activity.Rat lacrimal gland acini were incubated with H89, an inhibitor of protein kinase A, before the addition of dibutyryl cAMP (dbcAMP, 10(-3) M) for 30 minutes. Basal MAPK and CREB activity and MAPK activity after stimulation with the cholinergic agonist carbachol (Cch) or epidermal growth factor (EGF) for 5 minutes was determined. The effect of dbcAMP on EGF receptor activity and basal and stimulated Ras, Raf-1, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK), and MAPK activity was determined. The effect of a Rap-1 inhibitor, GGTI-298, on MAPK activity after the addition of dbcAMP was also determined.H89 relieved the inhibition of cAMP on MAPK activity and inhibited CREB activity. Incubation with dbcAMP did not have any effect either on the EGF receptor or on Ras but significantly inhibited both basal and Raf-1 and MEK activity stimulated with Cch or EGF. GGTI-298 did not have any effect on cAMP-dependent decrease in MAPK activity.The authors conclude that cAMP mediates the inhibition of MAPK by PKA in a Raf-1-dependent manner.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
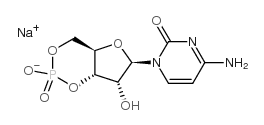 |
胞苷-3',5'-环一磷酸钠盐
CAS:54925-33-6 |
C9H11N3NaO7P |
|
Testosterone synthesized in cultured human SZ95 sebocytes de...
2010-05-01 [Exp. Dermatol. 19(5) , 470-2, (2010)] |
|
Genistein decreases androgen biosynthesis in rat Leydig cell...
2009-01-01 [Toxicol. Lett. 184(3) , 169-75, (2009)] |
|
Regulation of the system x(C)- cystine/glutamate exchanger b...
2011-10-01 [Glia 59(10) , 1387-401, (2011)] |
|
Cyclic cytidine 3',5'-monophosphate (cCMP) signals via cGMP ...
2010-09-24 [FEBS Lett. 584(18) , 3979-84, (2010)] |
|
Knockdown of hepatocyte aquaporin-8 by RNA interference indu...
2009-01-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 296(1) , G93-100, (2009)] |