Evidence for in situ and in vitro association between beta-dystroglycan and the subsynaptic 43K rapsyn protein. Consequence for acetylcholine receptor clustering at the synapse.
A Cartaud, S Coutant, T C Petrucci, J Cartaud
文献索引:J. Biol. Chem. 273(18) , 11321-6, (1998)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The accumulation of dystrophin and associated proteins at the postsynaptic membrane of the neuromuscular junction and their co-distribution with nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) clusters in vitro suggested a role for the dystrophin complex in synaptogenesis. Co-transfection experiments in which alpha- and beta-dystroglycan form a complex with AChR and rapsyn, a peripheral protein required for AChR clustering (Apel, D. A., Roberds, S. L., Campbell, K. P., and Merlie, J. P. (1995) Neuron 15, 115-126), suggested that rapsyn functions as a link between AChR and the dystrophin complex. We have investigated the interaction between rapsyn and beta-dystroglycan in Torpedo AChR-rich membranes using in situ and in vitro approaches. Cross-linking experiments were carried out to study the topography of postsynaptic membrane polypeptides. A cross-linked product of 90 kDa was labeled by antibodies to rapsyn and beta-dystroglycan; this demonstrates that these polypeptides are in close proximity to one another. Affinity chromatography experiments and ligand blot assays using rapsyn solubilized from Torpedo AChR-rich membranes and constructs containing beta-dystroglycan C-terminal fragments show that a rapsyn-binding site is present in the juxtamembranous region of the cytoplasmic tail of beta-dystroglycan. These data point out that rapsyn and dystroglycan interact in the postsynaptic membrane and thus reinforce the notion that dystroglycan could be involved in synaptogenesis.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
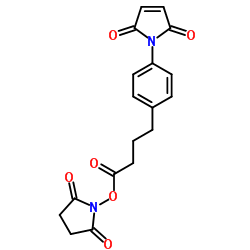 |
4-(4-马来酰亚胺基苯基)丁酸-N-琥珀酰亚胺酯
CAS:79886-55-8 |
C18H16N2O6 |
|
Development of pro-apoptotic peptides as potential therapy f...
2014-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 5 , 4478, (2014)] |
|
AFM imaging of immobilized fibronectin: does the surface con...
2014-04-22 [Langmuir 23(19) , 9745-51, (2007)] |
|
Herceptin-conjugated temperature-sensitive immunoliposomes e...
2016-03-01 [Arch. Pharm. Res. 39 , 350-8, (2016)] |
|
Size-Dependent Cellular Uptake of Trans-Activator of Transcr...
2016-03-01 [J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 12 , 536-45, (2016)] |
|
Optimisation of small-scale coupling of A5B7 monoclonal anti...
1993-01-14 [J. Immunol. Methods 158(1) , 49-56, (1993)] |