The weak immunosuppressant cyclosporine D as well as the immunologically inactive cyclosporine H are potent inhibitors in vivo of phorbol ester TPA-induced biological effects in mouse skin and of Ca2+/calmodulin dependent EF-2 phosphorylation in vitro.
M Gschwendt, W Kittstein, F Marks
文献索引:Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 150(2) , 545-51, (1988)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Various biological effects induced by the tumor promoting phorbol ester TPA in mouse skin are comparably suppressed by the immunologically inactive cyclosporine H (CsH) and by the strongly immunosuppressive cyclosporine A (CsA). These effects inhibited include the development of edema, stimulation of alkaline phosphatase activity, DNA and protein synthesis, as well as tumor promotion. Furthermore, CsH, like CsA, inhibits the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of the elongation factor 2 (EF-2) in vitro and the TPA-induced increases in the amount of EF-2 in vivo. Similar observations were made using the weak immunosuppressant CsD. We conclude from these results that the ability of cyclosporines to act as immunosuppressants and their ability to inhibit TPA-effects are based on two different mechanisms of action. Inhibition of TPA-effects may involve suppression of calmodulin-dependent processes, such as augmentation and phosphorylation of EF-2.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
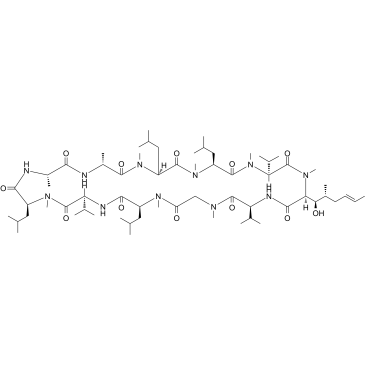 |
环孢菌素 D
CAS:63775-96-2 |
C63H113N11O12 |
|
Antimalarial activity of cyclosporins A, C and D.
1994-03-01 [Afr. J. Med. Med. Sci. 23(1) , 47-51, (1994)] |
|
Enzymatic synthesis of cyclosporin A.
1987-12-25 [J. Biol. Chem. 262(36) , 17258-9, (1987)] |
|
In vitro and in vivo comparative studies on immunosuppressiv...
1993-01-01 [Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 15(2-3) , 163-77, (1993)] |
|
Does the binding of cyclosporine to calmodulin result in imm...
1986-10-03 [Science 234(4772) , 68-71, (1986)] |
|
Synergistic effects of cyclosporin analogs--A, D, G, IMM-125...
2006-05-31 [Transplant. Proc. 26(5) , 3021-4, (1994)] |