Cardiotoxicity and prescription of thioridazine in New Zealand.
David B Menkes, James C Knight
文献索引:Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 36(4) , 492-8, (2002)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
To review the production of cardiac arrhythmia by thioridazine, and consider the role of government regulation in light of antipsychotic prescribing trends in New Zealand.We conducted a focused literature review on psychotropic-induced cardiotoxicity, including mechanisms and incidence. In addition, we considered trends in antipsychotic prescription in New Zealand and decisions made by regulatory bodies in Australia, North America and the United Kingdom regarding restrictions on the prescription of thioridazine.In general, the cardiotoxicity of antipsychotics, including thioridazine, relates to the ability of these drugs to antagonize voltage-sensitive potassium channels, and thereby prolong the QT interval. This action can lead to malignant arrhythmias in a very small proportion (< < 1%) of patients; the risk may be increased by other drugs or factors which prolong QT or inhibit the metabolism of thioridazine. A review of prescription doses and volumes in New Zealand indicates that thioridazine is prescribed mainly in low doses by non-specialists, and its use has been waning significantly over the past 2 years. These trends predate recent publicity regarding cardiotoxicity.Recommendations regarding thioridazine use are presented. Although new patients should not receive this drug, existing patients benefiting from modest doses should not be denied access unless clear-cut risk factors for cardiotoxicity are evident.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
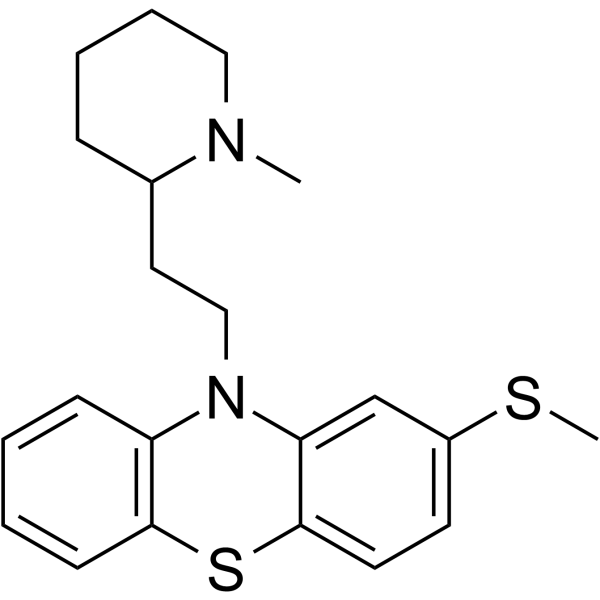 |
硫利达嗪
CAS:50-52-2 |
C21H26N2S2 |
|
[Simultaneous determination of 10 unapproved sedative drugs ...
2012-05-01 [Se Pu 30(5) , 457-62, (2012)] |
|
A repurposing approach identifies off-patent drugs with fung...
2013-02-01 [Eukaryotic Cell 12(2) , 278-87, (2013)] |
|
Why and how thioridazine in combination with antibiotics to ...
2012-08-01 [Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 10(8) , 869-73, (2012)] |
|
Synthesis, characterization and electrical properties of per...
2013-03-15 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 105 , 550-6, (2013)] |
|
Identification of drugs including a dopamine receptor antago...
2012-06-08 [Cell 149(6) , 1284-97, (2012)] |