A compact intermediate state of calmodulin in the process of target binding.
Yoshiteru Yamada, Tatsuhito Matsuo, Hiroyuki Iwamoto, Naoto Yagi
文献索引:Biochemistry 51(19) , 3963-70, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Calmodulin undergoes characteristic conformational changes by binding Ca(2+), which allows it to bind to more than 300 target proteins and regulate numerous intracellular processes in all eukaryotic cells. We measured the conformational changes of calmodulin upon Ca(2+) and mastoparan binding using the time-resolved small-angle X-ray scattering technique combined with flash photolysis of caged calcium. This measurement system covers the time range of 0.5-180 ms. Within 10 ms of the stepwise increase in Ca(2+) concentration, we identified a distinct compact conformational state with a drastically different molecular dimension. This process is too fast to study with a conventional stopped-flow apparatus. The compact conformational state was also observed without mastoparan, indicating that the calmodulin forms a compact globular conformation by itself upon Ca(2+) binding. This new conformational state of calmodulin seems to regulate Ca(2+) binding and conformational changes in the N-terminal domain. On the basis of this finding, an allosteric mechanism, which may have implications in intracellular signal transduction, is proposed.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
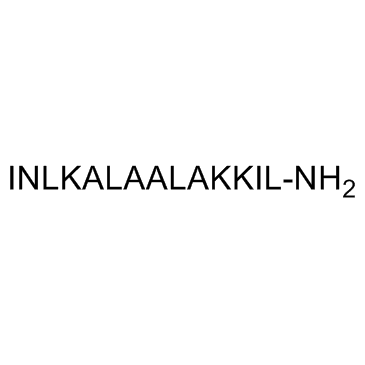 |
肥大脱粒肽
CAS:72093-21-1 |
C70H131N19O15 |
|
Axon targeting of the alpha 7 nicotinic receptor in developi...
2014-05-01 [J. Neurochem. 129(4) , 649-62, (2014)] |
|
The chloroplast calcium sensor CAS is required for photoaccl...
2011-08-01 [Plant Cell 23(8) , 2950-63, (2011)] |
|
Identification of the thiol isomerase-binding peptide, masto...
2013-04-12 [J. Biol. Chem. 288(15) , 10628-39, (2013)] |
|
Quantification of protein-protein interactions with chemical...
2011-04-01 [J. Proteome Res. 10(4) , 1528-37, (2011)] |
|
Heterotrimeric Gα(i) proteins are regulated by lipopolysacch...
2011-03-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1813(3) , 466-72, (2011)] |