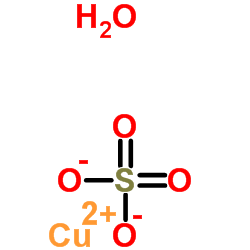
10257-54-2
| 中文名 | 硫酸铜 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | Copper sulfate monohydrate |
| 中文别名 | 硫酸铜一水合物 |
| 英文别名 |
Copper sulfate hydrate
Copper sulfate (5 water) CUPRICSULFATE,MONOHYDRATE,PURIFIED Copper(II) sulfate hydrate Copper(2+) sulfate hydrate (1:1:1) COPPER(II) SULFATE HYDRATE 98 |
| 沸点 | 330ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| 分子式 | CuH2O5S |
| 分子量 | 177.624 |
| 精确质量 | 176.891891 |
| PSA | 97.87000 |
| 外观性状 | 蓝色或绿色白色粉末 |
| 蒸汽压 | 3.35E-05mmHg at 25°C |
| 储存条件 | 贮存于干燥库房中 |
| 稳定性 | 加热到897~934℃分解成为氧化铜和三氧化硫。在干燥空气中慢慢风化变为白色粉状物。有毒。 |
| 分子结构 | 1、摩尔折射率:无可用的 2、摩尔体积(cm3/mol):无可用的 3、等张比容(90.2K):无可用的 4、表面张力(dyne/cm):无可用的 5、介电常数:无可用的 6、极化率(10-24cm3):无可用的 7、单一同位素质量:176.891894 Da 8、标称质量:177 Da 9、平均质量:177.6239 Da |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):无 2.氢键供体数量:1 3.氢键受体数量:5 4.可旋转化学键数量:0 5.互变异构体数量:无 6.拓扑分子极性表面积89.6 7.重原子数量:7 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:62.2 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:3 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:亮蓝色不对称三斜晶系结晶或粉末。 2. 密度(g/mL,25/4℃):2.284 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):不确定 4. 熔点(ºC):不确定 5. 沸点(ºC,0.67kpa或5 mmHg):不确定 6. 折射率:不确定 7. 闪点(ºC):不确定 8. 比旋光度(ºC):不确定 9. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC)不确定 10. 蒸气压(kPa,25ºC):不确定 11. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):不确定 12. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):不确定 13. 临界温度(ºC):不确定 14. 临界压力(KPa):不确定 15. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:不确定 16. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):不确定 17. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):不确定 18. 溶解性:易溶于水,微 溶于甲醇,不溶于无水乙醇。 |
|
Section 1. Chemical Product and Company Identification Cupric Sulfate, monohydrate Common Name/ Trade Name Manufacturer Commercial Name(s) Synonym
Chemical Name Chemical Family Cupric Sulfate, monohydrate Section 4. First Aid Measures Eye ContactCheck for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Cold water may be used. Get medical attention. Skin ContactIn case of contact, immediately flush skin with plenty of water. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. Remove contaminated clothing and shoes. Cold water may be used.Wash clothing before reuse. Thoroughly clean shoes before reuse. Get medical attention. Serious Skin ContactWash with a disinfectant soap and cover the contaminated skin with an anti-bacterial cream. Seek immediate medical attention. InhalationIf inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical attention. Serious InhalationNot available. IngestionDo NOT induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. If large quantities of this material are swallowed, call a physician immediately. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. Serious IngestionNot available. Section 5. Fire and Explosion Data Flammability of the Product Non-flammable. Auto-Ignition Temperature Not applicable. Flash PointsNot applicable. Flammable LimitsNot applicable. Products of CombustionNot available. Fire Hazards in Presence of Not applicable. Various Substances Explosion Hazards in Presence Risks of explosion of the product in presence of mechanical impact: Not available. of Various SubstancesRisks of explosion of the product in presence of static discharge: Not available. Fire Fighting MediaNot applicable. and Instructions Special Remarks onWhen heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes. Fire HazardsSolutions are acidic and can react with magnesium to evolve flammable hydrogen gas Special Remarks on Explosion Nitromethanes and copper salts spontaneously form explosive materials Hazards Section 6. Accidental Release Measures Small SpillUse appropriate tools to put the spilled solid in a convenient waste disposal container. Finish cleaning by spreading water on the contaminated surface and dispose of according to local and regional authority requirements. Large SpillUse a shovel to put the material into a convenient waste disposal container. Be careful that the product is not present at a concentration level above TLV. Check TLV on the MSDS and with local authorities. Cupric Sulfate, monohydrate Section 7. Handling and Storage PrecautionsDo not ingest. Do not breathe dust. Wear suitable protective clothing. In case of insufficient ventilation, wear suitable respiratory equipment. If ingested, seek medical advice immediately and show the container or the label. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Keep away from incompatibles such as metals, alkalis. StorageKeep container tightly closed. Keep container in a cool, well-ventilated area. Section 8. Exposure Controls/Personal Protection Engineering ControlsUse process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation, or other engineering controls to keep airborne levels below recommended exposure limits. If user operations generate dust, fume or mist, use ventilation to keep exposure to airborne contaminants below the exposure limit. Personal ProtectionSplash goggles. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent. Gloves. Personal Protection in Case of Splash goggles. Full suit. Dust respirator. Boots. Gloves. A self contained breathing apparatus should be used a Large Spillto avoid inhalation of the product. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a specialist BEFORE handling this product. Exposure LimitsTWA: 1 (mg/m3) from ACGIH (TLV) [United States] Inhalation TWA: 0.1 (mg/m3) from OSHA (PEL) [United States] Inhalation TWA: 1 (mg/m3) from NIOSH Inhalation Consult local authorities for acceptable exposure limits. Section 9. Physical and Chemical Properties Physical state and appearance Solid. (Powdered solid)OdorNot available. TasteNot available. 177.62 g/mole Molecular Weight ColorOff-white. pH (1% soln/water)Not available. Not available. Boiling Point Melting PointNot available. Not available. Critical Temperature Specific GravityNot available. Vapor PressureNot applicable. Vapor DensityNot available. VolatilityNot available. Odor ThresholdNot available. Water/Oil Dist. Coeff.Not available. Not available. Ionicity (in Water) Dispersion PropertiesSee solubility in water. SolubilitySoluble in cold water, hot water. Cupric Sulfate, monohydrate Section 10. Stability and Reactivity Data The product is stable. Stability Instability TemperatureNot available. Excess heat (high temperatures), incompatible materials, exposure to air Conditions of Instability Reactive with metals, alkalis. Incompatibility with various substances CorrosivityHighly corrosive in presence of steel. Special Remarks onSolutions of hyprobromite are decomposed by powerful catalytic action of cupric ions, even as impurities. ReactivityIncompatible with finely powdered metals, hydroxylamine, magnesium, acetylene, Sodium Hypobromite, and nitromethane. May react with acetylene to form dangerous acetylides. Can be corrosive to most ferrous based metals. Hygroscopic; keep container tightly closed. Corrosive to finely powdered metals. Special Remarks on CorrosivityVery corrosive to plain steel PolymerizationWill not occur. Section 11. Toxicological Information Routes of EntryInhalation. Ingestion. Toxicity to AnimalsLD50: Not available. LC50: Not available. Chronic Effects on Humans May cause damage to the following organs: kidneys, liver. Other Toxic Effects onHazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Humans Special Remarks onNot available. Toxicity to Animals Special Remarks onMay affect genetic material based on animal data. Chronic Effects on HumansMay cause adverse reproductive effects and birth defects (teratogenic) based on animal test data. May cause cancer based on animal test data Special Remarks on otherAcute Potential Health Effects: Toxic Effects on HumansSkin: Causes skin irritation. May cause skin burns. It may cause and itching allergic eczema. Eyes: Causes eye irritation. May cause eye burns. It may cause conjunctivitis, corneal discoloration, ulceration and turbidity of the cornea. Inhalation: Causes respiratory tract (nose, throat, lung) irritation with coughing and wheezing. May cause ulceration and perforation of the nasal septum if inhaled in excessive quantities. Burning copper sulfate may result in irritating and poisonous gases which may irritate the respiratory tract and lungs, and may cause fume metal fever which is characterized by flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, muscle aches. Ingestion: Harmful if swallowed. May cause gastrointestinal tract irritation with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, metallic taste, burning sensation in the stomach or epigastrum, abdominal pain, and possible gastrointestinal tract bleeding. May affect metabolism(metabolic acidosis), liver (liver damage, jaundice), blood (Methemoglobin, hemalytic anemia), urinary system (kidney damage, hematuria, hemoglobinuria, albuminuria), behavior/nervous systems (somnolence, tremor, psychosis, muscle weakness, coma), cardiovascular system (lowering of blood pressure, dysthrythmia). Oral mucosa, vomitus, stools, and saliva may be stained blue or green following ingestion. Aspiration pneumonia may develop following emesis and CNS depression. Chronic Potential Health Effects: Skin: Repeated or prolonged skin contact may cause thickening of the skin. Cupric Sulfate, monohydrate Section 12. Ecological Information EcotoxicityEcotoxicity in water (LC50): 0.1 ppm 48 hours [Goldfish].0.1 mg/l 96 hours [Rainbow Trout].2.5 mg/l 96 hours [Rainbow Trout]. BOD5 and CODNot available. Products of BiodegradationPossibly hazardous short term degradation products are not likely. However, long term degradation products may arise. Toxicity of the ProductsThe products of degradation are less toxic than the product itself. of Biodegradation If released to soil, copper sulfate may leach to groundwater, be partly oxidized, or bind to humic materials, clay, or Special Remarks on the Products of Biodegradationhydrous of iron and manganese. In water, it will bind to carbonates as well as humic materials, clay and hydrous oxides of iron and manganese. Copper is accumulated by plants and animals, but it does not appear to biomagnify from plants to animals. This lack of biomagnification appears common with heavy metals. In air, copper aerosols (in general) have a residence time of 2 to 10 days in an unpolluted atmosphere and 0.1 to >4 in a polluted, urban areas. Section 13. Disposal Considerations Copper dusts or mist or copper compounds may be disposed of in Group III sealed containers in a secure sanitary landfill. Copper containing Waste Disposal soluble wastes can be concentrated through the use of ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or evaporators to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and sent to a reclaiming firm. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated through the use of caustics and the sludge depositied in a chemical waste landfill. Be sure to consult with authorities (waste regulators). Waste must be disposed of in accordance with federal, state and local environmental control regulations. Section 14. Transport Information DOT ClassificationCLASS 9: Miscellaneous hazardous material. : Environmentally hazardous substance, n.o.s. (Cupric Sulfate) UNNA: 3077 PG: III Identification Special Provisions foradditional markings "Marine Pollutant" - required for bulk shipments. The words "Marine Pollutant" must be Transportentered on the shipping paper in association iwth the basic DOT description for bulk shipments. DOT (Pictograms) Section 15. Other Regulatory Information and Pictograms Federal and StateSARA 313 toxic chemical notification and release reporting: Copper compounds CERCLA: Hazardous substances.: Cupric Sulfate, monohydrate: 10 lbs. (4.536 kg) Regulations CaliforniaCalifornia prop. 65: This product contains the following ingredients for which the State of California has found Proposition 65to cause cancer which would require a warning under the statute: No products were found. Warnings California prop. 65: This product contains the following ingredients for which the State of California has found to cause birth defects which would require a warning under the statute: No products were found. Other RegulationsOSHA: Hazardous by definition of Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200). WHMIS (Canada) CLASS D-2B: Material causing other toxic effects (TOXIC). Other Classifications DSCL (EEC)R22- Harmful if swallowed.S22- Do not breathe dust. R36/38- Irritating to eyes and skin.S60- This material and its container must be R50/53- Very toxic to aquaticdisposed of as hazardous waste. organisms, may cause long-termS61- Avoid release to the environment. Refer to adverse effects in the aquaticspecial instructions/Safety data sheets. environment. Cupric Sulfate, monohydrate Health Hazard HMIS (U.S.A.)2 National Fire Protection 0 Flammability 0 Association (U.S.A.) Fire Hazard 2 0 Reactivity Health Reactivity 0 Specific hazard Personal Protection E WHMIS (Canada) (Pictograms) DSCL (Europe) (Pictograms) TDG (Canada) (Pictograms) ADR (Europe) (Pictograms) Protective Equipment Gloves. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent. Splash goggles. SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION N/A |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
|
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xn: Harmful;N: Dangerous for the environment; |
|---|---|
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | R22;R36/38;R50/53 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S22-S60-S61 |
| 危险品运输编码 | UN 3077 |
| 海关编码 | 2833250000 |
| 海关编码 | 2833250000 |
|---|