丙基膦酸

丙基膦酸结构式

|
常用名 | 丙基膦酸 | 英文名 | propylphosphonic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 4672-38-2 | 分子量 | 124.07600 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | 265.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C3H9O3P | 熔点 | 67-71 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 114.3ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS05 |
信号词 | Danger |
| 中文名 | 丙基膦酸 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | propylphosphonic acid |
| 中文别名 | 丙烷-1-磷酸 | 丙基磷酸 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 沸点 | 265.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| 熔点 | 67-71 °C(lit.) |
| 分子式 | C3H9O3P |
| 分子量 | 124.07600 |
| 闪点 | 114.3ºC |
| 精确质量 | 124.02900 |
| PSA | 67.34000 |
| LogP | 0.57410 |
| InChIKey | NSETWVJZUWGCKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCP(=O)(O)O |
| 储存条件 | 避光,通风干燥处,密封保存 |
| 稳定性 | 常温常压下稳定,熔点: 133-136°C |
| 分子结构 | 1、 摩尔折射率:25.89 2、 摩尔体积(m3/mol):97.2 3、 等张比容(90.2K):257.0 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm):48.9 5、 极化率(10 -24cm 3):10.26 |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):-0.7 2.氢键供体数量:2 3.氢键受体数量:3 4.可旋转化学键数量:2 5.互变异构体数量:无 6.拓扑分子极性表面积57.5 7.重原子数量:7 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:84.2 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:白色粉末 2. 密度(g/mL,25 ºC):不确定 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):不确定 4. 熔点(ºC):133-136 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):不确定 6. 沸点(ºC,21mmHg):不确定 7. 折射率:不确定 8. 闪点(ºC):不确定 9. 比旋光度(º,C=1, H2O):不确定 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):不确定 11. 蒸气压(kPa,25ºC):不确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):不确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):不确定 14. 临界温度(ºC):不确定 15. 临界压力(KPa):不确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:不确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):不确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):不确定 19. 溶解性:不确定 |
|
丙基膦酸毒理学数据: 1 、急性毒性:大鼠口径LDLo:3723 mg/kg 2、主要的刺激性影响 在皮肤上面:在皮肤和粘膜上造成腐蚀性影响 在眼睛上面:强烈腐蚀性影响 致敏作用:没有已知的敏化影响 丙基膦酸生态学数据: 通常对水是不危害的,若无政府许可,勿将材料排入周围环境 |
| 符号 |

GHS05 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Danger |
| 危害声明 | H314 |
| 警示性声明 | P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| 个人防护装备 | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | C |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | 34 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S26-S36/37/39-S45 |
| 危险品运输编码 | UN 3260 8/PG 3 |
| WGK德国 | 1 |
| RTECS号 | TA0420000 |
| 包装等级 | III |
| 危险类别 | 8 |
|
In situ derivatization hollow fiber mediated liquid phase microextraction of alkylphosphonic acids from water.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1141(2) , 151-7, (2007) Alkylphosphonic acids (APAs), particularly the methyl-, ethyl-, isopropyl- and n-propyl-phosphonic acids are important markers of extremely toxic nerve agents. Hence, their detection and identificatio... |
|
|
Inactivation of Aeromonas hydrophila by Fe(II)-related-radical generation in oxidizing groundwaters.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62(9) , 3277-83, (1996) The survival of Aeromonas hydrophila AWWX1 in filter-sterilized phreatic groundwaters was studied by using viable counts. Aeromonas counts rapidly decreased 2 to 3 log units in oxidizing raw groundwat... |
|
|
A validated method for the quantification of fosfomycin in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 990 , 164-8, (2015) Fosfomycin is a small, hydrophilic antibiotic drug with activity against Gram-positive as well as Gram-negative pathogens. It is in increasing use in intensive care units as a last line antibiotic sin... |
| propanephosphonic acid |
| EINECS 225-121-8 |
| MFCD00012294 |
| 1-propanephosphonic acid |
| propylphosphoric acid |
| Propane-1-phosphonic acid |
| Propyl-phosphonic acid |
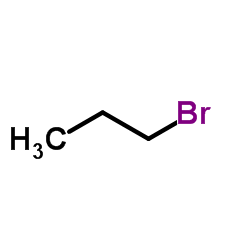 CAS号106-94-5
CAS号106-94-5 CAS号75779-78-1
CAS号75779-78-1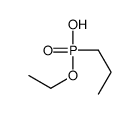 CAS号21921-96-0
CAS号21921-96-0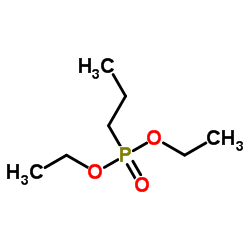 CAS号18812-51-6
CAS号18812-51-6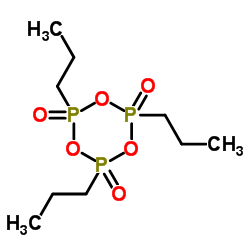 CAS号68957-94-8
CAS号68957-94-8 CAS号18755-43-6
CAS号18755-43-6
