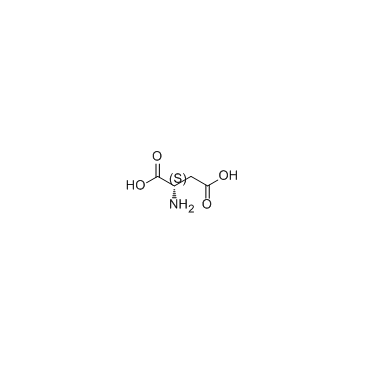
2-胍基琥珀酸
2-胍基琥珀酸结构式

|
常用名 | 2-胍基琥珀酸 | 英文名 | Guanidinosuccinic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 6133-30-8 | 分子量 | 175.143 | |
| 密度 | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 344.5±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C5H9N3O4 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 162.1±30.7 °C |
2-胍基琥珀酸用途Guanidinosuccinic acid 是从血清和尿液中分离出的含氮代谢物,在尿毒症患者的尿液和血清中升高。 |
| 中文名 | 2-胍基琥珀酸 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | N-amidino-L-aspartic acid |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | Guanidinosuccinic acid 是从血清和尿液中分离出的含氮代谢物,在尿毒症患者的尿液和血清中升高。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 体内研究 | 胍基琥珀酸是正常尿液的一种成分,在尿毒症患者的尿液和血清中升高[1]。胍基琥珀酸(GSA)是一种发现在尿毒症中大大增加的胍基化合物,通过腹膜内(ip)注射给予成年白化小鼠和7,14和21日龄的幼鼠。评估致痫性和毒性特性并确定ip注射后的胍基琥珀酸脑水平。在成年小鼠中,胍基琥珀酸以剂量依赖性方式诱导持久的全身性阵挛性阵挛和阵挛-强直性惊厥,CD50(和95%置信区间)为363(287-458)mg/kg(n = 35), LD50为579(445-756)mg/kg。胍基琥珀酸的CD50对应于脑浓度为56nmol/g组织。五只成年小鼠的脑电图记录显示癫痫样放电(尖刺,尖刺波和多刺波)与痉挛同时出现,当年轻小鼠腹腔注射(成人)亚惊厥剂量的胍基琥珀酸(250 mg/kg) ),在胍基琥珀酸诱导的惊厥和由此产生的脑浓度[2]中发现年龄依赖性降低。 |
| 动物实验 | 小鼠[2]在标准的环境控制条件下饲养随机繁殖的瑞士小鼠(雄性和雌性,第一系列实验的体重13-25g)。对于另一系列实验,使用7,14和21天龄的年轻瑞士小鼠。注射胍基琥珀酸悬浮液的体积为0.1mL / 10g体重,ip,剂量为250-1000mg / kg(每剂5只小鼠,一式两份)。注射后,将小鼠置于单独的圆柱形透明笼中并观察1小时(在幼小鼠的情况下观察2小时)。 CD50和LD50都是通过概率单位分析或移动平均插值计算的[2]。 |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 344.5±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 分子式 | C5H9N3O4 |
| 分子量 | 175.143 |
| 闪点 | 162.1±30.7 °C |
| 精确质量 | 175.059311 |
| PSA | 136.50000 |
| LogP | -1.50 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.633 |
| 储存条件 | 2-8℃ |
| 个人防护装备 | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| 海关编码 | 2925290090 |
|
~% 
2-胍基琥珀酸 6133-30-8 |
| 文献:Pant,E. Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift fuer Physiologische Chemie, 1964 , vol. 335, p. 272 - 274 |
|
~% 
2-胍基琥珀酸 6133-30-8 |
| 文献:Ratner et al. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1953 , vol. 204, p. 95,108 |
|
~% 
2-胍基琥珀酸 6133-30-8 |
| 文献:Walker Archives of Biochemistry, 1955 , vol. 59, p. 233,234, 240 |
| 2-胍基琥珀酸上游产品 4 | |
|---|---|
| 2-胍基琥珀酸下游产品 0 | |
| 海关编码 | 2925290090 |
|---|---|
| 中文概述 | 2925290090 其他亚胺及其衍生物,以及它们的盐。监管条件:无。增值税率:17.0%。退税率:9.0%。最惠国关税:6.5%。普通关税:30.0% |
| 申报要素 | 品名, 成分含量, 用途 |
| Summary | 2925290090 other imines and their derivatives; salts thereof。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Uraemic guanidino compounds inhibit gamma-aminobutyric acid-evoked whole cell currents in mouse spinal cord neurones.
Neurosci. Lett. 265(2) , 83-6, (1999) Guanidine, creatinine (CTN), methylguanidine (MG) and guanidinosuccinic acid (GSA) are four endogenous guanidino compounds with proven neuroexcitatory actions, and putative pathophysiological signific... |
|
|
Effect of NaCN on currents evoked by uremic retention solutes in dissociated mouse neurons.
Brain Res. 1008(1) , 107-12, (2004) Uremic retention solutes possibly contribute to neuronal hypoxia/ischemia and its consequences in patients with renal failure. We examined the in vitro effects of several uremic retention solutes on m... |
|
|
Accumulation of methylguanidine and changes in guanidino compound levels in plasma, urine, and kidneys of furosemide-treated rats.
Metab. Clin. Exp. 57(6) , 802-10, (2008) Antidiuresis and renal diseases alter the levels of guanidino compounds (GCs) in various tissues. Therefore, we hypothesized that diuresis could also disturb GC metabolism, storage, and elimination. I... |
| N-Carbamimidoyl-L-asparaginsaeure |
| N-amidinoaspartic acid |
| L-Aspartic acid, N-(aminoiminomethyl)- |
| aspartic acid, N-(aminoiminomethyl)- |
| N-Amidino-L-aspartic acid |
| 2-Guanidinosuccinic acid |
| GUANIDINOSUCCINIC ACID |
| (2S)-2-carbamimidamidobutanedioic acid |
| Aspartic acid, N-(diaminomethylene)- |
| N-Carbamimidoyl-L-aspartic acid |
| N-(Diaminomethylene)aspartic acid |
| N-Carbamimidoylaspartic acid |
| n-amidino-asparticaci |