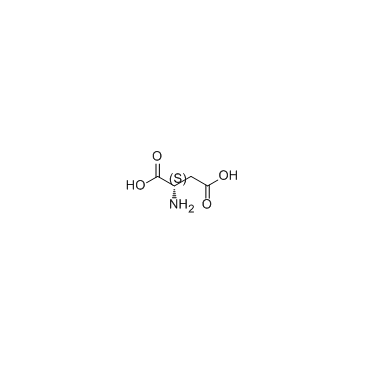
Guanidinosuccinic acid
Guanidinosuccinic acid structure
|
Common Name | Guanidinosuccinic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6133-30-8 | Molecular Weight | 175.143 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 344.5±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9N3O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 162.1±30.7 °C | |
Use of Guanidinosuccinic acidGuanidinosuccinic acid is a nitrogenous metabolite isolated in excess from serum and urine. |
| Name | N-amidino-L-aspartic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Guanidinosuccinic acid is a nitrogenous metabolite isolated in excess from serum and urine. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Guanidinosuccinic acid, a constituent of normal urine, is elevated in the urine and serum of azotemic patients[1]. Guanidinosuccinic acid (GSA), a guanidino compound found to be greatly increased in uremia, is administered by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection to adult albino mice and to young mice 7, 14 and 21 days old. Epileptogenic and toxic properties are assessed and Guanidinosuccinic acid brain levels following i.p. injection ae determined. In adult mice, Guanidinosuccinic acid induces long-lasting generalized clonic and clonic-tonic convulsions in a dose-dependent manner with a CD50 (and 95% confidence interval) of 363 (287-458) mg/kg (n=35), and an LD50 of 579 (445-756) mg/kg. The CD50 of Guanidinosuccinic acid corresponded with a brain concentration of 56 nmol/g tissue. Electrocorticographic recording in five adult mice revealed epileptiform discharges (spikes, spike-waves, and polyspike-waves) which appeared concomitant with the convulsions, When young mice are i.p. injected with a (for adults) subconvulsive dose of Guanidinosuccinic acid (250 mg/kg), an age-dependent decrease is noted in Guanidinosuccinic acid-induced convulsions and in the resulting brain concentration[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Randomly bred Swiss mice (male and female, body weight 13-25 g for the first series of experiments) are housed under standard environmentally controlled conditions. For another series of experiments, young Swiss mice 7, 14 and 21 days old are used. Injections of Guanidinosuccinic acid suspensions are delivered in volumes of 0.1 mL per 10 g body weight, i.p. and in doses between 250 and 1000 mg/kg (5 mice per dose, in duplicate). After injection, the mice are put in individual cylindrical transparent cages and observed for 1 h (for 2 h in the case of the young mice). Both CD50 and LD50 are calculated by probit analysis or moving average interpolation[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 344.5±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 175.143 |
| Flash Point | 162.1±30.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 175.059311 |
| PSA | 136.50000 |
| LogP | -1.50 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.633 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|
~% 
Guanidinosuccin... CAS#:6133-30-8 |
| Literature: Pant,E. Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift fuer Physiologische Chemie, 1964 , vol. 335, p. 272 - 274 |
|
~% 
Guanidinosuccin... CAS#:6133-30-8 |
| Literature: Ratner et al. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1953 , vol. 204, p. 95,108 |
|
~% 
Guanidinosuccin... CAS#:6133-30-8 |
| Literature: Walker Archives of Biochemistry, 1955 , vol. 59, p. 233,234, 240 |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2925290090 other imines and their derivatives; salts thereof。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Uraemic guanidino compounds inhibit gamma-aminobutyric acid-evoked whole cell currents in mouse spinal cord neurones.
Neurosci. Lett. 265(2) , 83-6, (1999) Guanidine, creatinine (CTN), methylguanidine (MG) and guanidinosuccinic acid (GSA) are four endogenous guanidino compounds with proven neuroexcitatory actions, and putative pathophysiological signific... |
|
|
Effect of NaCN on currents evoked by uremic retention solutes in dissociated mouse neurons.
Brain Res. 1008(1) , 107-12, (2004) Uremic retention solutes possibly contribute to neuronal hypoxia/ischemia and its consequences in patients with renal failure. We examined the in vitro effects of several uremic retention solutes on m... |
|
|
Accumulation of methylguanidine and changes in guanidino compound levels in plasma, urine, and kidneys of furosemide-treated rats.
Metab. Clin. Exp. 57(6) , 802-10, (2008) Antidiuresis and renal diseases alter the levels of guanidino compounds (GCs) in various tissues. Therefore, we hypothesized that diuresis could also disturb GC metabolism, storage, and elimination. I... |
| N-Carbamimidoyl-L-asparaginsaeure |
| N-amidinoaspartic acid |
| L-Aspartic acid, N-(aminoiminomethyl)- |
| aspartic acid, N-(aminoiminomethyl)- |
| N-Amidino-L-aspartic acid |
| 2-Guanidinosuccinic acid |
| GUANIDINOSUCCINIC ACID |
| (2S)-2-carbamimidamidobutanedioic acid |
| Aspartic acid, N-(diaminomethylene)- |
| N-Carbamimidoyl-L-aspartic acid |
| N-(Diaminomethylene)aspartic acid |
| N-Carbamimidoylaspartic acid |
| n-amidino-asparticaci |