α-半乳糖苷酶
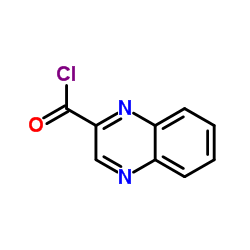
α-半乳糖苷酶结构式

|
常用名 | α-半乳糖苷酶 | 英文名 | α-galactosidase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 9025-35-8 | 分子量 | 192.602 | |
| 密度 | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 324.4±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C9H5ClN2O | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | 闪点 | 150.0±22.3 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
α-半乳糖苷酶用途α-半乳糖苷酶(EC 3.2.1.22),即α-半乳糖糖苷酶,是一种广泛存在于动物、植物和微生物中的糖苷水解酶,常用于生化研究。α-半乳糖苷酶催化α-1,6-连接的末端半乳糖残基的水解,包括低聚半乳糖、半乳甘露聚糖和半乳糖脂质。催化许多分解代谢过程,包括糖蛋白、糖脂和多糖的裂解[1]。 |
| 中文名 | α-半乳糖苷酶 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | alpha-Galactosidase |
| 中文别名 | 蜜二糖酶 | Α-半乳糖苷酶(+4℃) | Α-D-半乳糖苷半乳糖水解酶 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | α-半乳糖苷酶(EC 3.2.1.22),即α-半乳糖糖苷酶,是一种广泛存在于动物、植物和微生物中的糖苷水解酶,常用于生化研究。α-半乳糖苷酶催化α-1,6-连接的末端半乳糖残基的水解,包括低聚半乳糖、半乳甘露聚糖和半乳糖脂质。催化许多分解代谢过程,包括糖蛋白、糖脂和多糖的裂解[1]。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 324.4±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 分子式 | C9H5ClN2O |
| 分子量 | 192.602 |
| 闪点 | 150.0±22.3 °C |
| 精确质量 | 192.009033 |
| LogP | 2.12 |
| 外观性状 | buffered aqueous solution |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.663 |
| 储存条件 | 2-8°C密闭、阴凉干燥处 |
| 稳定性 | Unit Definition One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole of p-nitrophenyl α-D-galactoside to p-nitrophenol and D-galactose per min at pH 6.5 at 25 °C. Physical form Suspension in 3.2 M (NH4)2SO4 solution, pH 6.0, containing BSA |
| 更多 | 1. 性状: 悬浮在pH值为6.0其中载有牛血清白蛋白的3.2M(硫酸铵)硫酸铵溶液。 2. 密度(g/mL,25℃):未确定 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):未确定 4. 熔点(ºC):未确定 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):未确定 6. 沸点(ºC,5.2kPa):未确定 7. 折射率:未确定 8. 闪点(ºC):未确定 9. 比旋光度(º):未确定 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):未确定 11. 蒸气压(kPa,20ºC):未确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):未确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):未确定 14. 临界温度(ºC):未确定 15. 临界压力(KPa):未确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:未确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):未确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):未确定 19. 溶解性:溶于水 |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Warning |
| 危害声明 | H315-H319-H335 |
| 警示性声明 | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xi |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | 36/37/38 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | 36/37-26 |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK德国 | 3 |
|
High throughput screening for inhibitors of alpha-galactosidase.
Curr. Chem. Genomics 4 , 67-73, (2011) Fabry disease is a rare X-linked lysosomal storage disorder caused by a deficiency in α-galactosidase A (GLA), which catalyzes the hydrolysis of terminal α-galactosyl groups from glycosphingolipids, s... |
|
|
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling and microvascular dysfunction in the mesentery of mice deficient in α-galactosidase A.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 306(2) , G140-6, (2014) A defect in the gene for the lysosomal enzyme α-galactosidase A (Gla) results in globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) accumulation in Fabry disease and leads to premature death from cardiac and cerebrovascular... |
|
|
Long-term effect of antibodies against infused alpha-galactosidase A in Fabry disease on plasma and urinary (lyso)Gb3 reduction and treatment outcome.
PLoS ONE 7(10) , e47805, (2012) Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) with alpha-Galactosidase A (aGal A) may cause antibody (AB) formation against aGal A in males with Fabry disease (FD). Anti agalsidase ABs negatively influence globotr... |
| Agalsidase |
| E.C. 3.2.1.22 |
| alpha-Galactoside galactohydrolase |
| Melibiase |
| 2-Quinoxalinecarbonyl chloride |
| quinoxaline-2-carbonyl chloride |
| alpha-D-Galactosidase |
| alpha-GAL 600L |
| alpha-D-Galactopyranosidase |
| Alpha-Gal 1000 |
| Validase AGS |
| alpha-D-Galactoside galactohydrolase |
| Alpha Gal 500 |
| alpha-Galactosidase A |
| Sumizyme AGS |


