Silver-nanoparticles increase bactericidal activity and radical oxygen responses against bacterial pathogens in human osteoclasts
Valerie Aurore, Fabienne Caldana, Marianne Blanchard, Solange Kharoubi Hess, Nils Lannes, Pierre-Yves Mantel, Luis Filgueira, Michael Walch
Index: 10.1016/j.nano.2017.11.006
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
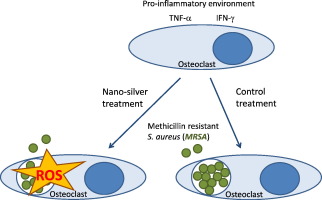
Bone infections are difficult to treat and can lead to severe tissue destruction. Acute bone infections are usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Osteoclasts, which belong to the monocyte/macrophage lineage, are the key cells in bone infections. They are not well equipped for killing bacteria and may serve as a reservoir for bacterial pathogens. Silver has been known for centuries for its bactericidal activity. Here, we investigated the bactericidal effects of nano-silver particles in bacteria infected human osteoclasts. We found that nano-silver in per se non-toxic concentration enhanced the bactericidal activity in osteoclasts against intracellular Methicillin-resistant, virulent Staphylococcus aureus. The reduced bacterial survival in nano-silver pretreated cells correlated with increased reactive oxygen responses towards the invading pathogens. Overall, these results indicate that nano-silver compounds should be considered as an effective treatment and prevention option for bacterial bone and orthopedic implant infections.
|
High sensitive and multiple detection of Acute Myocardial In...
2018-03-28 [10.1016/j.nano.2018.02.013] |
|
Screening for canine transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) by SE...
2018-03-27 [10.1016/j.nano.2018.03.001] |
|
Nanomagnetic Modulation of Tumor Redox State ☆
2018-03-26 [10.1016/j.nano.2018.03.002] |
|
Polymersome nanoparticles for delivery of Wnt-activating sma...
2018-03-17 [10.1016/j.nano.2018.02.014] |
|
In Vitro Studies of Heparin-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles fo...
2018-03-08 [10.1016/j.nano.2018.02.011] |