The Journal of Organic Chemistry
2018-04-13
Synthesis of 1-Cyanoalkynes and Their Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed Cycloaddition with Organic Azides to Afford 4-Cyano-1,2,3-triazoles
Peiye Liu, Ronald J. Clark, Lei Zhu
Index: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b00424
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
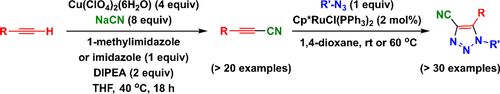
A new method to convert terminal alkynes under relatively mild conditions to 1-cyanoalkynes using in situ formed cyanogen is described. 1-Cyanoalkynes have a higher reactivity than terminal alkynes in the ruthenium(II)-catalyzed regiospecific azide–alkyne cycloaddition to afford 4-cyano-1,2,3-triazoles. A mechanistic proposal different from the one that terminal alkynes adopt under the same reaction conditions is proposed. This work provides a new and convenient two-step sequence to prepare 4-cyano-1,2,3-triazoles from terminal alkynes and organic azides.
Latest Articles:
More...
|
Synthesis and Unique Optical Properties of Selenophenyl BODI...
2018-04-19 [10.1021/acs.joc.8b00782] |
|
Synthesis of 3,5-Disubstituted BODIPYs Bearing N-Containing ...
2018-04-17 [10.1021/acs.joc.8b00087] |
|
Steric Hindrance Underestimated: It is a Long, Long Way to T...
2018-04-17 [10.1021/acs.joc.8b00496] |
|
Stereoselective Sequential [4+2]/[2+2] Cycloadditions Involv...
2018-04-16 [10.1021/acs.joc.8b00346] |
|
Pd-Induced Double C–H Bond Activation in Annulative Synthese...
2018-04-16 [10.1021/acs.joc.8b00630] |