Liquid Phase Hydrodeoxygenation of Anisole, 4-Ethylphenol and Benzofuran Using Ni, Ru and Pd Supported on USY Zeolite
David P. Gamliel, Stavros Karakalos, Julia A. Valla
Index: 10.1016/j.apcata.2018.04.004
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
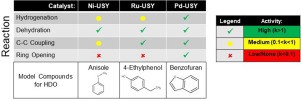
The objective of this work is to understand the role of metals on the hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) reaction pathways of three bio-oil model compounds. Ni, Ru and Pd were impregnated on USY zeolite, and the catalysts were characterized to determine metal reduction profile, surface concentration and nanoparticle size. Ru-USY and Pd-USY were completely reduced at a temperature below 450 °C, but Ni-USY still contained surface metal oxides after reduction. There was no indication of strong interactions between the metals and USY support. Anisole, 4-ethylphenol and benzofuran were used as bio-oil model compounds, in order to determine the effects of each metal on deoxygenation of methoxy-, phenol and furan functional groups, respectively. Pd-USY was the most effective HDO catalyst, exhibiting the highest turnover frequency for HDO of all three model compounds, in addition to and high selectivity to deoxygenated products. A mechanism was proposed for each model compound, and the kinetics of hydrogenation, dehydration, C-C coupling and ring-opening reactions were determined.
|
MFI zeolite coating with intrazeolitic aluminum (acidic) gra...
2018-04-09 [10.1016/j.apcata.2018.04.006] |
|
Construction of Novel Cu/ZnO-Al2O3 Composites for Furfural H...
2018-04-07 [10.1016/j.apcata.2018.04.005] |
|
Photocatalytic and Photochemical Processes on the Surface of...
2018-03-29 [10.1016/j.apcata.2018.03.015] |
|
Impact of the presence of Mo carbide species prepared ex sit...
2018-03-29 [10.1016/j.apcata.2018.03.023] |
|
Dehydration of D-xylose into furfural over bimetallic salts ...
2018-03-27 [10.1016/j.apcata.2018.03.027] |