| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
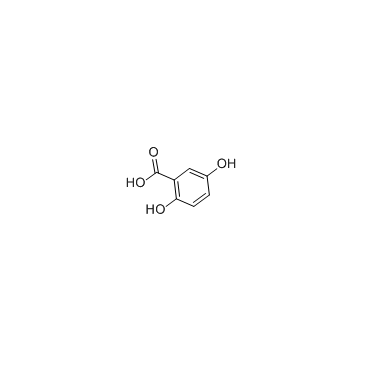 |
Gentisic acid
CAS:490-79-9 |
|
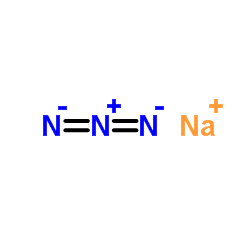 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
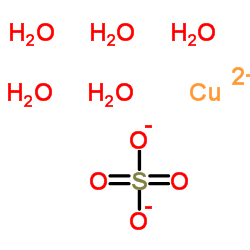 |
Cupric sulfate
CAS:7758-98-7 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
 |
MES
CAS:4432-31-9 |