| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
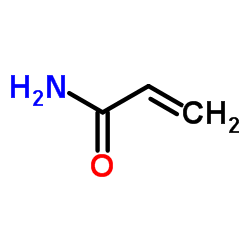 |
Acrylamide Crystals
CAS:79-06-1 |
|
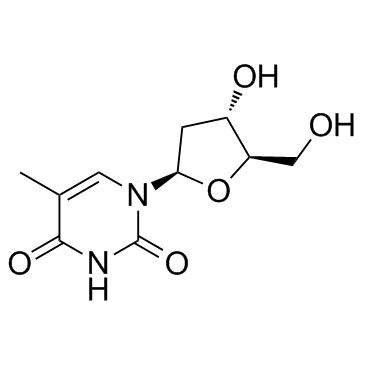 |
Thymidine
CAS:50-89-5 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
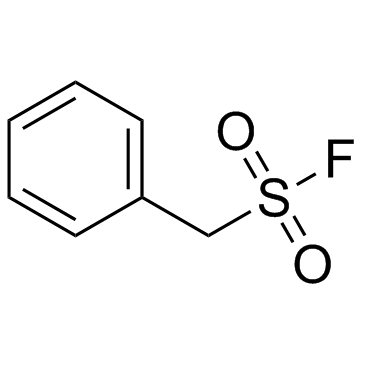 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
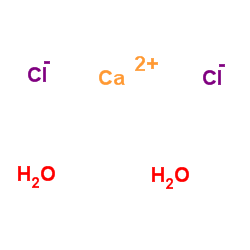 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |