| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
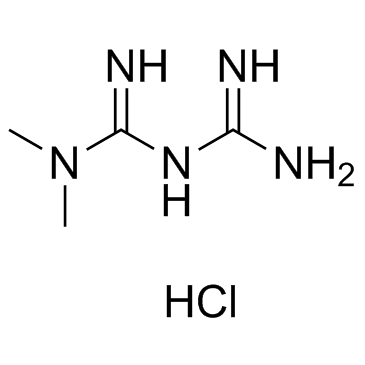 |
Metformin HCl
CAS:1115-70-4 |
|
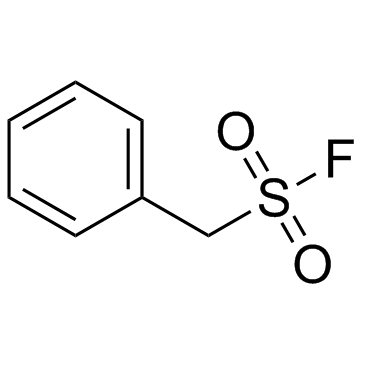 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |