| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
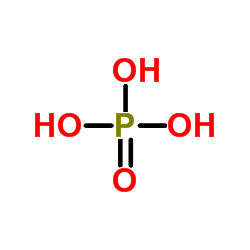 |
Phosphoric acid
CAS:7664-38-2 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Formaldehyde
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
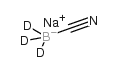 |
sodium cyanoborodeuteride
CAS:25895-62-9 |
|
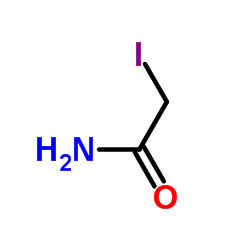 |
Iodoacetamide
CAS:144-48-9 |
|
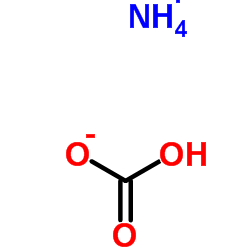 |
Ammonium Bicarbonate
CAS:1066-33-7 |
|
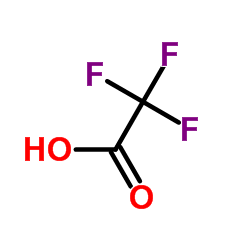 |
trifluoroacetic acid
CAS:76-05-1 |