| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
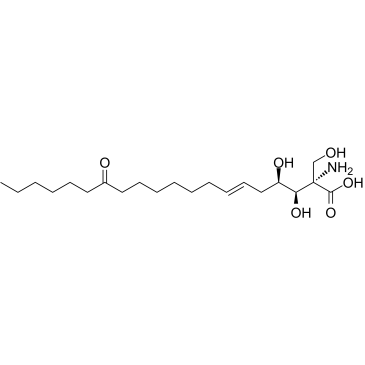 |
Myriocin
CAS:35891-70-4 |
|
 |
Sodium deoxycholate
CAS:302-95-4 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
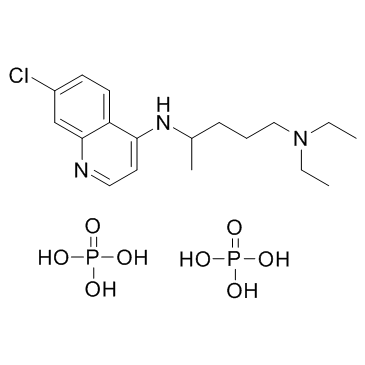 |
Chloroquine diphosphate
CAS:50-63-5 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
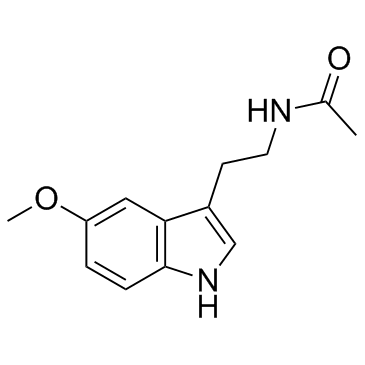 |
Melatonine
CAS:73-31-4 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |