| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
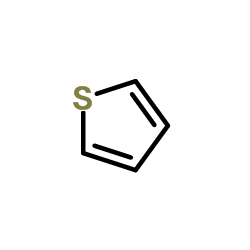 |
Thiophene
CAS:110-02-1 |
|
 |
N-hexane
CAS:110-54-3 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
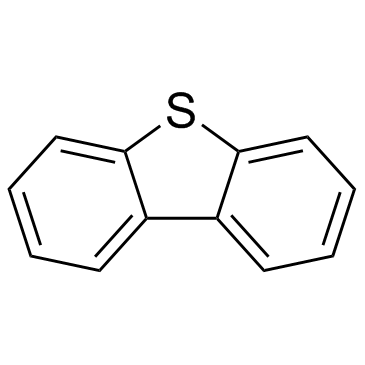 |
Dibenzothiophene
CAS:132-65-0 |
|
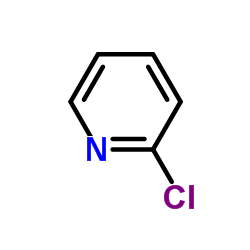 |
2-Chloropyridine
CAS:109-09-1 |
|
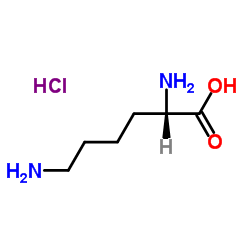 |
L-Lysine hydrochloride
CAS:10098-89-2 |
|
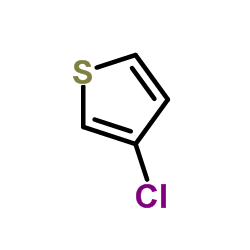 |
3-Chlorothiophene
CAS:17249-80-8 |