| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium carbonate
CAS:497-19-8 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
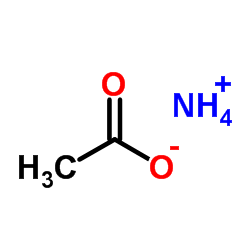 |
Ammonium acetate
CAS:631-61-8 |
|
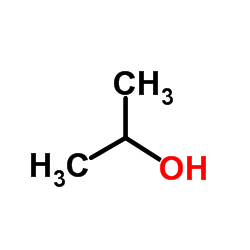 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
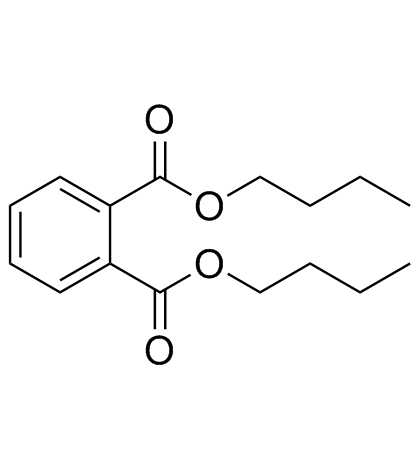 |
1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid
CAS:84-74-2 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
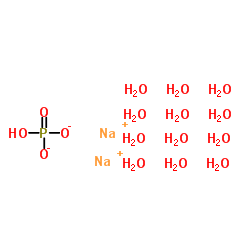 |
Disodium phosphate dodecahydrate
CAS:10039-32-4 |
|
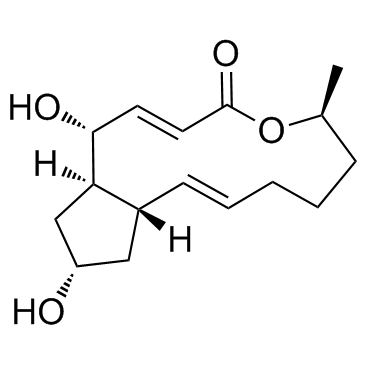 |
Brefeldin A
CAS:20350-15-6 |
|
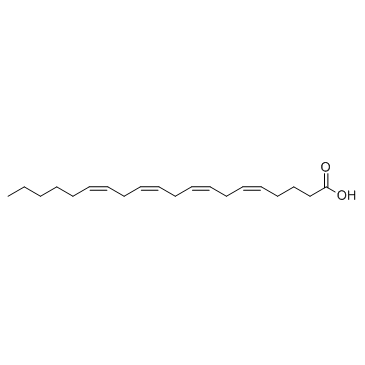 |
Arachidonic acid
CAS:506-32-1 |