| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
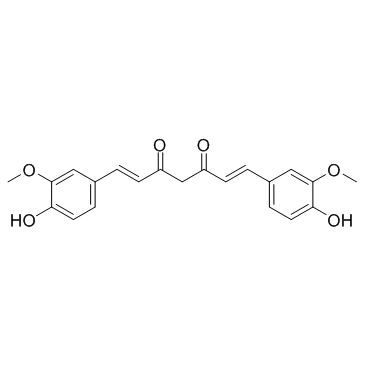 |
Curcumin
CAS:458-37-7 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
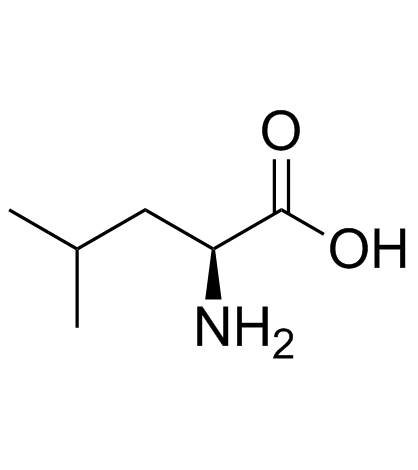 |
L-leucine
CAS:61-90-5 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
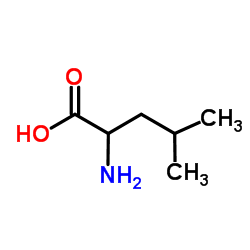 |
2-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
CAS:328-39-2 |