| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
dichloroethane
CAS:107-06-2 |
|
 |
8-Aminopyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic Acid
CAS:196504-57-1 |
|
 |
3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane
CAS:919-30-2 |
|
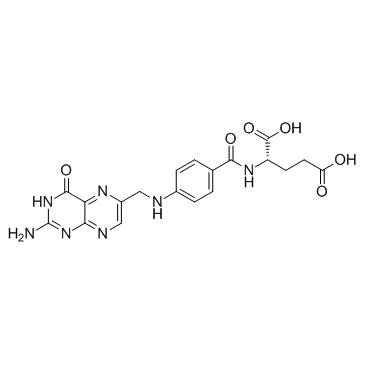 |
Folic Acid
CAS:59-30-3 |
|
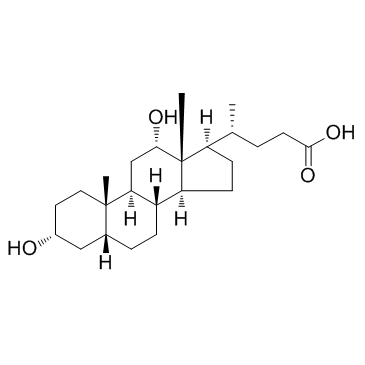 |
Deoxycholic acid
CAS:83-44-3 |