Implications for the kynurenine pathway and quinolinic acid in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Gilles J Guillemin, Vincent Meininger, Bruce J Brew
Index: Neurodegener. Dis. 2(3-4) , 166-76, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The kynurenine pathway (KP) is a major route of L-tryptophan catabolism leading to production of several neurobiologically active molecules. Among them is the excitotoxin quinolinic acid (QUIN) that is known to be involved in the pathogenesis of several major inflammatory neurological diseases. In amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) degeneration of motor neurons is associated with a chronic and local inflammation (presence of activated microglia and astrocytes). There is emerging evidence that the KP is important in ALS. Recently, we demonstrated that QUIN is significantly increased in serum and CSF of ALS patients. Moreover, most of the factors associated with QUIN toxicity are found in ALS, implying that QUIN may play a substantial role in the neuropathogenesis of ALS. This review details the potential role the KP has in ALS and advances a testable hypothetical model.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
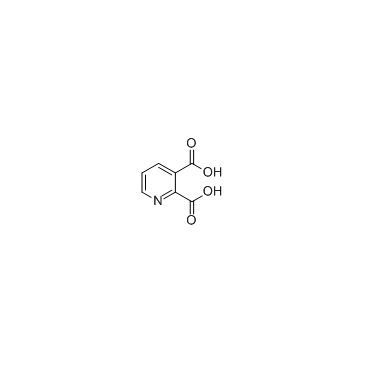 |
Quinolinic acid
CAS:89-00-9 |
C7H5NO4 |
|
The CB₁ cannabinoid receptor signals striatal neuroprotectio...
2015-10-01 [Cell Death Differ. 22 , 1618-29, (2015)] |
|
Activation of the kynurenine pathway and increased productio...
2015-01-01 [J. Neuroinflammation 12 , 110, (2015)] |
|
Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a ...
1994-06-01 [Clin. Chem. 40(6) , 862-6, (1994)] |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state ...
2007-05-01 [Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007)] |
|
Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine ...
2009-02-12 [Nature 457(7231) , 910-4, (2009)] |