Quinolinic acid
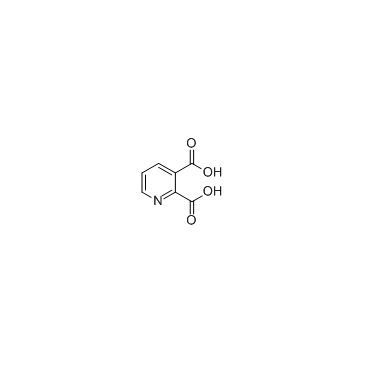
Quinolinic acid structure
|
Common Name | Quinolinic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 89-00-9 | Molecular Weight | 167.119 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 425.0±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5NO4 | Melting Point | 188-190ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 210.9±24.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Quinolinic acidQuinolinic acid is an endogenous N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor agonist synthesized from L-tryptophan via the kynurenine pathway and thereby has the potential of mediating N-methyl-D-aspartate neuronal damage and dysfunction. |
| Name | quinolinic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Quinolinic acid is an endogenous N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor agonist synthesized from L-tryptophan via the kynurenine pathway and thereby has the potential of mediating N-methyl-D-aspartate neuronal damage and dysfunction. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 425.0±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 188-190ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 167.119 |
| Flash Point | 210.9±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 167.021851 |
| PSA | 87.49000 |
| LogP | -1.44 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.628 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Water Solubility | 0.55 g/100 mL |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | US7967250 |
| HS Code | 29333999 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
The CB₁ cannabinoid receptor signals striatal neuroprotection via a PI3K/Akt/mTORC1/BDNF pathway.
Cell Death Differ. 22 , 1618-29, (2015) The CB1 cannabinoid receptor, the main molecular target of endocannabinoids and cannabis active components, is the most abundant G protein-coupled receptor in the mammalian brain. In particular, the C... |
|
|
Activation of the kynurenine pathway and increased production of the excitotoxin quinolinic acid following traumatic brain injury in humans.
J. Neuroinflammation 12 , 110, (2015) During inflammation, the kynurenine pathway (KP) metabolises the essential amino acid tryptophan (TRP) potentially contributing to excitotoxicity via the release of quinolinic acid (QUIN) and 3-hydrox... |
|
|
Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a healthy Turkish pediatric population.
Clin. Chem. 40(6) , 862-6, (1994) Organic acid concentrations were quantified by gas chromatography and the individual acids identified by mass spectrometry in urine specimens from a healthy Turkish pediatric population of ages 2 days... |
| 2,3-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid |
| MFCD00006295 |
| EINECS 201-874-8 |
| Quinolinic acid |
| UNII-F6F0HK1URN |
| T6NJ BVQ CVQ |
| Pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid |
 CAS#:91-22-5
CAS#:91-22-5 CAS#:98-98-6
CAS#:98-98-6 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9 CAS#:2050-22-8
CAS#:2050-22-8 CAS#:18704-37-5
CAS#:18704-37-5 CAS#:148-24-3
CAS#:148-24-3 CAS#:548-93-6
CAS#:548-93-6 CAS#:91-63-4
CAS#:91-63-4 CAS#:91-62-3
CAS#:91-62-3 CAS#:611-32-5
CAS#:611-32-5![Pyrido[2,3-d]pyridazine-5,8-diol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/118/4430-77-7.png) CAS#:4430-77-7
CAS#:4430-77-7 CAS#:36052-27-4
CAS#:36052-27-4 CAS#:321-02-8
CAS#:321-02-8 CAS#:4664-00-0
CAS#:4664-00-0 CAS#:498-95-3
CAS#:498-95-3 CAS#:82949-15-3
CAS#:82949-15-3 CAS#:4043-87-2
CAS#:4043-87-2 CAS#:18970-62-2
CAS#:18970-62-2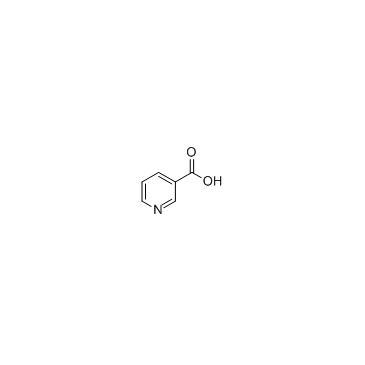 CAS#:59-67-6
CAS#:59-67-6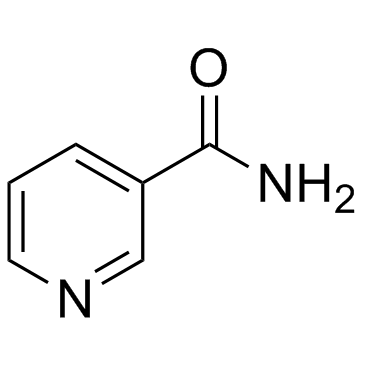 CAS#:98-92-0
CAS#:98-92-0
