| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
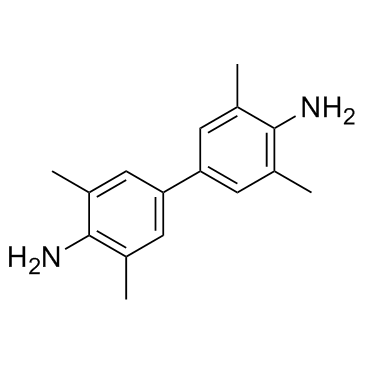 |
Tetramethylbenzidine
CAS:54827-17-7 |
|
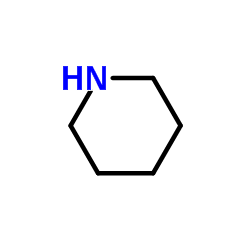 |
Piperidine
CAS:110-89-4 |
|
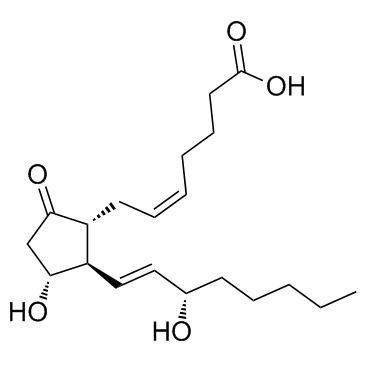 |
Dinoprostone
CAS:363-24-6 |
|
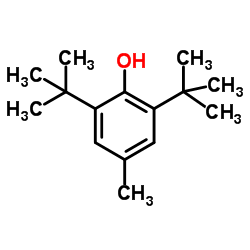 |
Butylated hydroxytoluene
CAS:128-37-0 |
|
 |
Rosiglitazone
CAS:122320-73-4 |
|
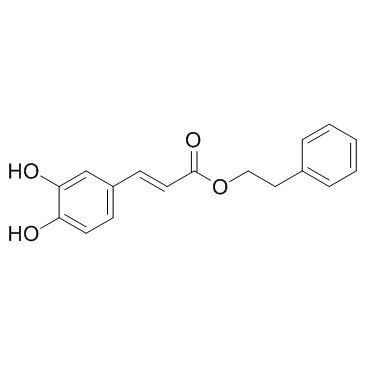 |
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester
CAS:104594-70-9 |