| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
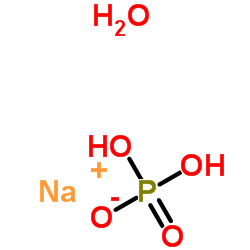 |
Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate
CAS:10049-21-5 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
potassium chloride
CAS:7447-40-7 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
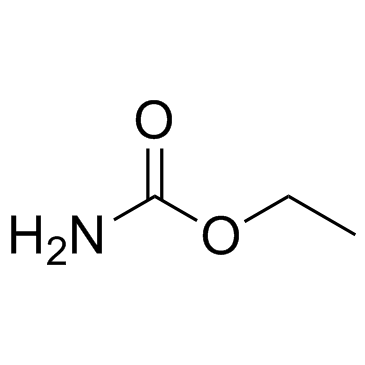 |
Urethane
CAS:51-79-6 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
 |
magnesium sulfate
CAS:7487-88-9 |
|
 |
Sodium metabisulfite
CAS:7681-57-4 |