| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
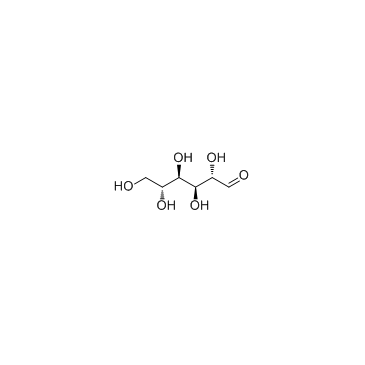 |
D-Mannose
CAS:3458-28-4 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
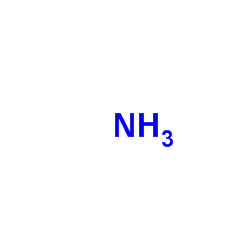 |
Ammonia
CAS:7664-41-7 |
|
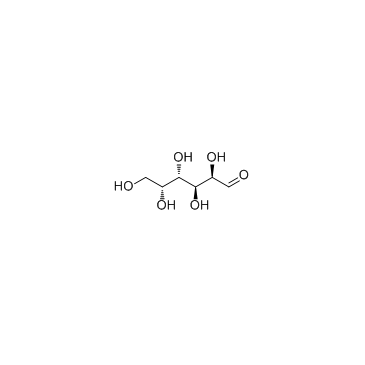 |
D-Galactose
CAS:59-23-4 |