| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
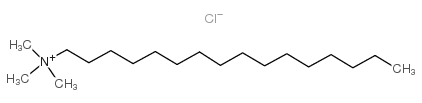 |
N-Hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride
CAS:112-02-7 |
|
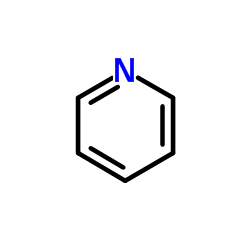 |
Pyridine
CAS:110-86-1 |
|
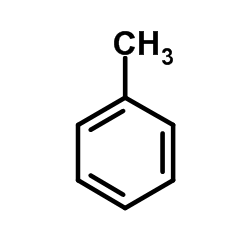 |
Toluene
CAS:108-88-3 |
|
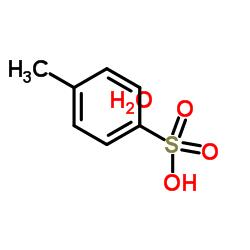 |
p-Toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate
CAS:6192-52-5 |
|
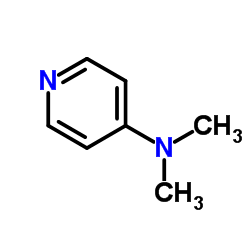 |
4-Dimethylaminopyridine
CAS:1122-58-3 |