| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
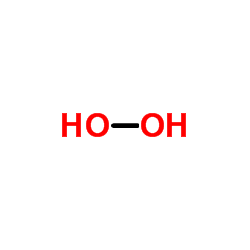 |
Hydrogen peroxide
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
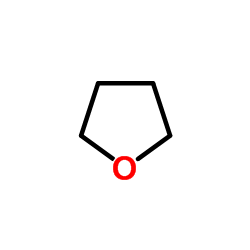 |
thf
CAS:109-99-9 |
|
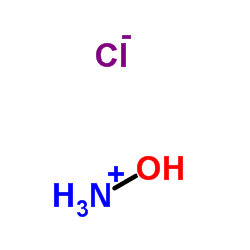 |
Hydroxyamine hydrochloride
CAS:5470-11-1 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |