| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
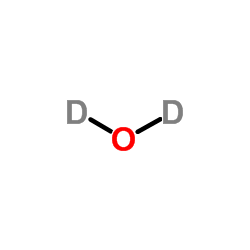 |
Heavy water
CAS:7789-20-0 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
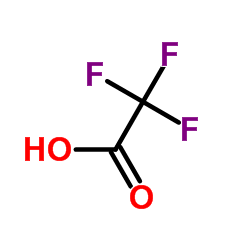 |
trifluoroacetic acid
CAS:76-05-1 |
|
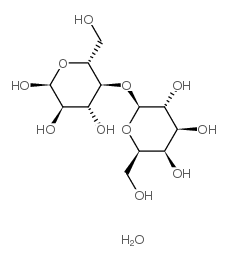 |
D-(+)-Lactose Monohydrate
CAS:64044-51-5 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Trehalose dihydrate
CAS:6138-23-4 |