| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
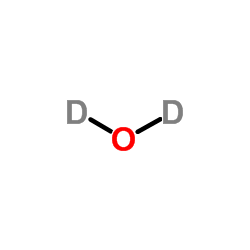 |
Heavy water
CAS:7789-20-0 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
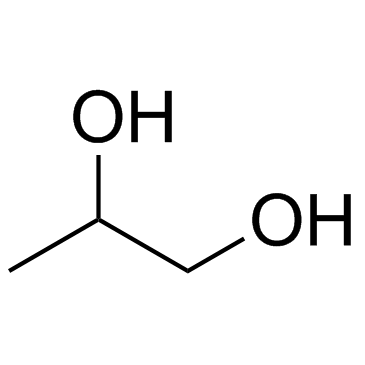 |
Propylene Glycol
CAS:57-55-6 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
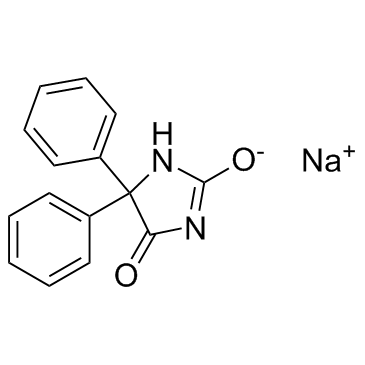 |
Phenytoin sodium
CAS:630-93-3 |