| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
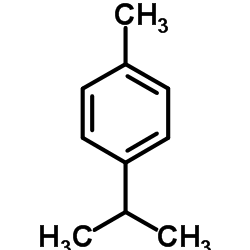 |
p-cymene
CAS:99-87-6 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
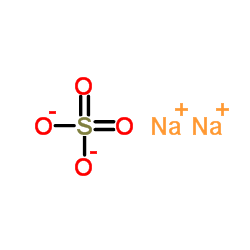 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
 |
Fructose
CAS:57-48-7 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
 |
(+)-Camphene
CAS:79-92-5 |
|
 |
Sabinene
CAS:3387-41-5 |