| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
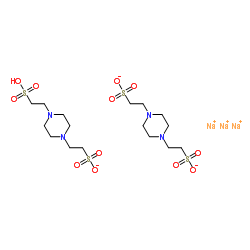 |
PIPES
CAS:5625-37-6 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
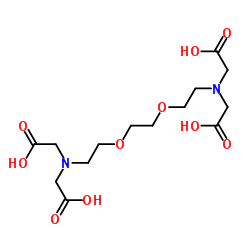 |
EGTA
CAS:67-42-5 |
|
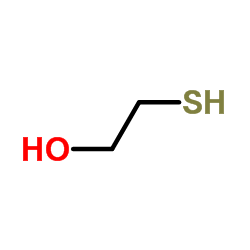 |
mercaptoethanol
CAS:60-24-2 |
|
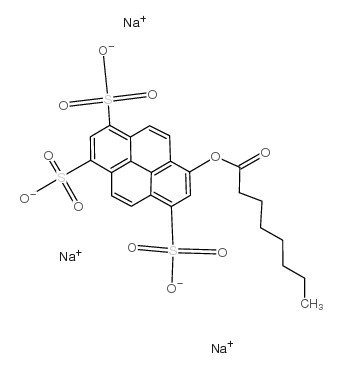 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |