| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Salbutamol
CAS:18559-94-9 |
|
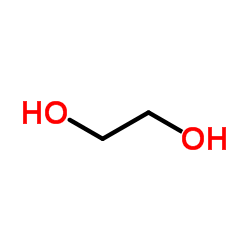 |
Ethylene glycol
CAS:107-21-1 |
|
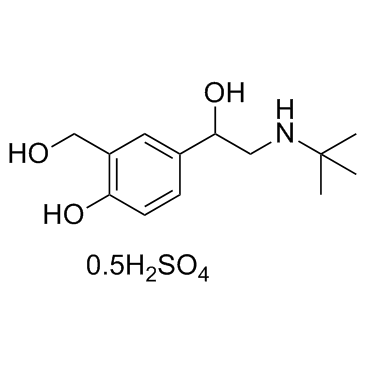 |
Albuterol sulfate
CAS:51022-70-9 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
3-(3-Hydroxy-1-oxo-2-phenylpropoxy)-8-methyl-8-(1-methylethyl)-8-azoniabicyclo(3.2.1)octane bromide monohydrate
CAS:66985-17-9 |